
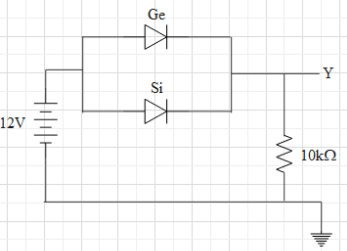
Two junction diodes one of germanium (Ge) and other of silicon (Si) are connected as shown in the figure, to a battery of emf 12V and a load resistance $10k\Omega $. The germanium diode conducts at 0.3V and silicon diode at 0.7V. When a current flows in the circuit, the potential of terminal Y will be:
A. 12V
B. 11V
C. 11.3V
D. 11.7V

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Check whether the diodes are in forward biased or reverse biased condition. Then find the potential difference across the diode. Since the negative terminal of the battery is grounded, it will be at potential of 0V. The current will flow through that diode with less resistance.
Complete answer:
In the figure, we can see that the p (anode terminal) sides of both the diodes are connected to the positive terminal of the battery. And the n sides (cathode terminal) of the both the diodes are connected to the negative side of the battery. This means that the anodes of the diodes are at a higher potential than that of the cathodes, which implies that both the diodes are in forward biased condition. This means both of them will allow current to pass through them.
However, we see that the diodes are in parallel connection, which means that both of them must have equal potential difference across them. We see that both the diodes have different voltages for which they conduct. Now, what will happen is that current will find the easiest path to travel. In other words, it will flow through that diode with less resistance. The diode having lower conducting voltage, will provide less resistance. In this case, the Ge diode has less conducting voltage. Therefore, the current will only pass through the Ge diode and potential difference across the diodes will be 0.3V.
We see in the figure that the negative terminal of the battery is grounded. This means that the negative terminal of the battery is at a potential of 0V. Therefore, the positive terminal of the battery is at a potential of 12V. And we just found that the potential drop of 0.3V across the diodes.Therefore, the potential at Y is $12-0.3=11.7V$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: Current always flows from a point of higher potential to a point of lower potential. Therefore, when a diode is forward biased, current flows from its anode to its cathode. When the anode of the diode is at lower potential than that of its cathode, we say that the diode is reverse biased. A diode does not allow any current pass through when reverse biased.
Complete answer:
In the figure, we can see that the p (anode terminal) sides of both the diodes are connected to the positive terminal of the battery. And the n sides (cathode terminal) of the both the diodes are connected to the negative side of the battery. This means that the anodes of the diodes are at a higher potential than that of the cathodes, which implies that both the diodes are in forward biased condition. This means both of them will allow current to pass through them.
However, we see that the diodes are in parallel connection, which means that both of them must have equal potential difference across them. We see that both the diodes have different voltages for which they conduct. Now, what will happen is that current will find the easiest path to travel. In other words, it will flow through that diode with less resistance. The diode having lower conducting voltage, will provide less resistance. In this case, the Ge diode has less conducting voltage. Therefore, the current will only pass through the Ge diode and potential difference across the diodes will be 0.3V.
We see in the figure that the negative terminal of the battery is grounded. This means that the negative terminal of the battery is at a potential of 0V. Therefore, the positive terminal of the battery is at a potential of 12V. And we just found that the potential drop of 0.3V across the diodes.Therefore, the potential at Y is $12-0.3=11.7V$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: Current always flows from a point of higher potential to a point of lower potential. Therefore, when a diode is forward biased, current flows from its anode to its cathode. When the anode of the diode is at lower potential than that of its cathode, we say that the diode is reverse biased. A diode does not allow any current pass through when reverse biased.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




