
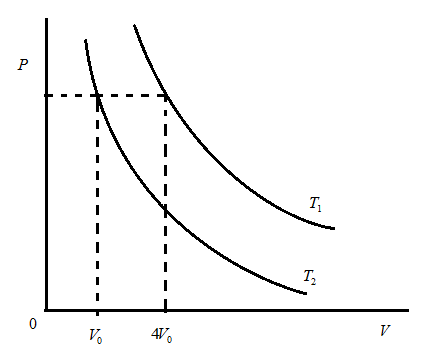
Two isotherms are drawn at temperature $ {T_1} $ and $ {T_2} $ as shown. The ratio of mean speed at $ {T_1} $ and $ {T_2} $ is:
(A) $ 1:4 $
(B) $ 1:2 $
(C) $ 2:1 $
(D) $ 4:1 $

Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: Here, the graph between pressure and volume is of isotherms at temperatures $ {T_1} $ and $ {T_2} $. We have to understand the meaning of isotherm in thermodynamics, a curve on a P-V diagram representing the state of a gas at constant temperature. Now, we have to use the terms shown in the above diagram and also the concept that volume is directly proportional to the root of temperature.
i.e. $ V \propto \sqrt T $
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the above diagram as shown above:
Above graph is the isothermal graph which is between pressure and volume. This graph shows that there are two temperature curves of $ {T_1} $ and $ {T_2} $ .
In the isothermal process volume of the substance is directly proportional to the root of temperature such that $ V \propto \sqrt T $ using this we are going to discuss about the ratio between two volumes such that:
$ V \propto \sqrt T $
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} \propto \sqrt {{T_1}} $ and $ {V_2} \propto \sqrt {{T_2}} $
Now, we know that $ PV = nRT $
From this we know that $ T \propto V $
$ \therefore $ The ratio between the volumes $ {V_1} $ and $ {V_2} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{V_0}} }}{{\sqrt {{V_0}} }} $ … $ \because \left( {{T_1} = 4{V_0},{T_2} = {V_0}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4{{{V}}_0}}}{{{{{V}}_0}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{2}{1} $
After solving all the equations above we concluded that $ {V_1}:{V_2} = 2:1 $
The ratio between the volumes is $ 2:1 $
The correct answer is option C.
Note:
Here, we must understand the concept in isotherm that it is given by the change in volume but same in temperature. We have understood the concept that volume is directly proportional to the temperature by the ideal gas equation. We have to be careful about the calculation.
i.e. $ V \propto \sqrt T $
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the above diagram as shown above:
Above graph is the isothermal graph which is between pressure and volume. This graph shows that there are two temperature curves of $ {T_1} $ and $ {T_2} $ .
In the isothermal process volume of the substance is directly proportional to the root of temperature such that $ V \propto \sqrt T $ using this we are going to discuss about the ratio between two volumes such that:
$ V \propto \sqrt T $
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} \propto \sqrt {{T_1}} $ and $ {V_2} \propto \sqrt {{T_2}} $
Now, we know that $ PV = nRT $
From this we know that $ T \propto V $
$ \therefore $ The ratio between the volumes $ {V_1} $ and $ {V_2} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {4{V_0}} }}{{\sqrt {{V_0}} }} $ … $ \because \left( {{T_1} = 4{V_0},{T_2} = {V_0}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4{{{V}}_0}}}{{{{{V}}_0}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{2}{1} $
After solving all the equations above we concluded that $ {V_1}:{V_2} = 2:1 $
The ratio between the volumes is $ 2:1 $
The correct answer is option C.
Note:
Here, we must understand the concept in isotherm that it is given by the change in volume but same in temperature. We have understood the concept that volume is directly proportional to the temperature by the ideal gas equation. We have to be careful about the calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




