
Two identical metal balls A and B moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point $X$ as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their
1. Shape
2. Speed
3. Direction
4. Volume
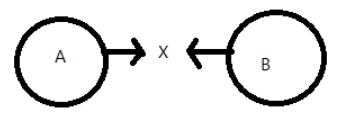
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{.1 and 3} \\
& \text{B}\text{.2 and 3} \\
& \text{C}\text{.2 and 4} \\
& \text{D}\text{. 1,2 and 3} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: We are given two identical metal balls which undergo collision. During a collision there is an interaction between the bodies, which results in transfer of momentum and energy between the bodies.
Complete answer:
We know that collision is the interaction between two bodies which are moving with some velocities for a short duration of time. We also know that when two identical bodies undergo collision there is a transfer of momentum and energy between the bodies. Generally, collision results in the change in velocity of the interacting bodies. Since velocity is a vector, we can say that collion changes the direction and speed of the interacting bodies.
We know from the conservation of momentum, that the total momentum of the system remains unchanged. However, the kinetic energy of the system depends on the type of collision occurring.
Collision can be broadly classified into two types of collision namely the elastic collision, and the inelastic collision.
In elastic collision, both the momentum and the kinetic energy of the system is conserved.
In inelastic collisions, the momentum of the system is conserved while the kinetic energy is not conserved.
Here we have two identical bodies which undergo collision.Then we can say that the direction and the speed of the balls changes after the collision.
Hence the answer is \[\text{B}\text{.2 and 3}\].
Note:
Here, we are given identical bodies, however the same can be applied to two bodies of different mass and speed. Then, clearly we can say that the body of greater mass will affect the momentum and the speed of the smaller body.
Complete answer:
We know that collision is the interaction between two bodies which are moving with some velocities for a short duration of time. We also know that when two identical bodies undergo collision there is a transfer of momentum and energy between the bodies. Generally, collision results in the change in velocity of the interacting bodies. Since velocity is a vector, we can say that collion changes the direction and speed of the interacting bodies.
We know from the conservation of momentum, that the total momentum of the system remains unchanged. However, the kinetic energy of the system depends on the type of collision occurring.
Collision can be broadly classified into two types of collision namely the elastic collision, and the inelastic collision.
In elastic collision, both the momentum and the kinetic energy of the system is conserved.
In inelastic collisions, the momentum of the system is conserved while the kinetic energy is not conserved.
Here we have two identical bodies which undergo collision.Then we can say that the direction and the speed of the balls changes after the collision.
Hence the answer is \[\text{B}\text{.2 and 3}\].
Note:
Here, we are given identical bodies, however the same can be applied to two bodies of different mass and speed. Then, clearly we can say that the body of greater mass will affect the momentum and the speed of the smaller body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




