
Two geometrical isomers are given by the following compound
A. Ethylidene bromide
B. Acetylene tetrachloride
C. Acetylene tetrabromide
D. Acetylene dibromide
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: The chemical which has the same chemical formula and exists in different forms is called isomers. The compounds or chemicals which have a double bond in its structure generally show geometrical isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is asked which molecules among the given options will show two geometrical isomers.
- To find it we have to draw each and every structure of the compound given in the options.
- Coming to option A, Ethylidiene bromide.
- The structure of ethylidene bromide is as follows:
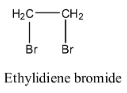
- In the above structure we can clearly see that there is no double bond present in it.
- Therefore option A does not show that geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option B, acetylene tetrachloride.
- The structure of acetylene tetrachloride is as follows.
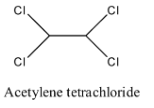
- In the structure of option B, there is no double bond.
- Therefore acetylene tetrachloride is not going to exhibit geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option C, Acetylene tetrabromide.
- The structure of Acetylene tetrabromide is as follows:
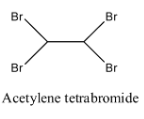
- In the structure of option C, there is no double bond.
- Therefore acetylene tetrabromide is not going to exhibit geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option D, Acetylene dibromide.
- The structure of Acetylene dibromide is as follows.
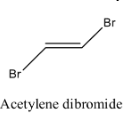
- In the structure of the acetylene dibromide there is a presence of double bond.
- Therefore acetylene dibromide is going to show geometrical isomerism.
- The geometrical isomerism of the compound acetylene dibromide is as follows.
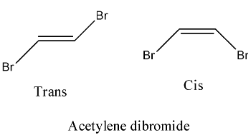
Therefore option D is correct.
Note: The compound which exhibits geometrical isomerism shows two types of isomers. The two types of geometrical isomers are cis and trans. Trans form of a compound is more stable then the cis form because of the less steric hindrance.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is asked which molecules among the given options will show two geometrical isomers.
- To find it we have to draw each and every structure of the compound given in the options.
- Coming to option A, Ethylidiene bromide.
- The structure of ethylidene bromide is as follows:

- In the above structure we can clearly see that there is no double bond present in it.
- Therefore option A does not show that geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option B, acetylene tetrachloride.
- The structure of acetylene tetrachloride is as follows.

- In the structure of option B, there is no double bond.
- Therefore acetylene tetrachloride is not going to exhibit geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option C, Acetylene tetrabromide.
- The structure of Acetylene tetrabromide is as follows:

- In the structure of option C, there is no double bond.
- Therefore acetylene tetrabromide is not going to exhibit geometrical isomerism.
- Coming to option D, Acetylene dibromide.
- The structure of Acetylene dibromide is as follows.

- In the structure of the acetylene dibromide there is a presence of double bond.
- Therefore acetylene dibromide is going to show geometrical isomerism.
- The geometrical isomerism of the compound acetylene dibromide is as follows.

Therefore option D is correct.
Note: The compound which exhibits geometrical isomerism shows two types of isomers. The two types of geometrical isomers are cis and trans. Trans form of a compound is more stable then the cis form because of the less steric hindrance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




