
Two different compounds having the molecular formula \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{8}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{15}}}}{\rm{Br}}\] are formed when \[{\rm{1,6}}\]-dimethyl-cyclohexene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the dark and in the absence of per-oxides. The same two compounds are formed from \[{\rm{1,2}}\]-dimethyl-cyclohexene. What are these compounds?
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that compounds with the same molecular formula but differ in structures are known as constitutional isomers.
Complete answer
According to Anti Markovnikov rule or peroxide effect or Kharasch effect, when unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide, the bromide ion will join to the carbon carrying more hydrogen atom while hydrogen ion will go to the other carbon atom.
The two different compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structures are known as constitutional isomers. The different structures may have different stereochemistry or different group attachment.
Now, alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the dark and in the absence of per-oxides gives products according to Markovnikov rule. So, when \[{\rm{1,6}}\]- dimethyl-cyclohexene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the dark and in the absence of per-oxides, the bromide ion will join to the carbon carrying less hydrogen atom while hydrogen ion will go to the other carbon but there is an exception that more substituted carbocations are more stable and undergo rearrangement by \[{\rm{1 - 2}}\] hydrogen shift as-
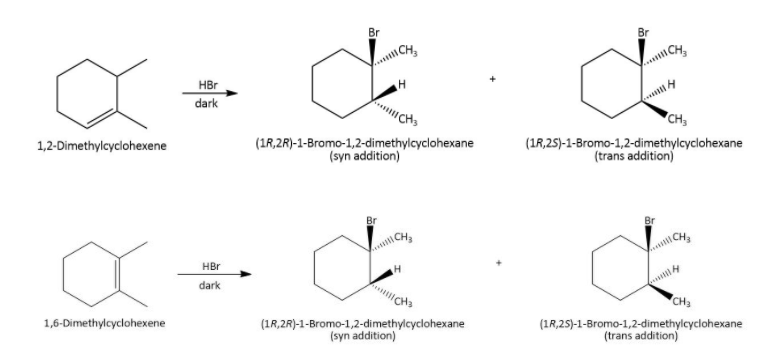
Therefore, the compounds are \[{\rm{(1R,2R)}}\,{\rm{1 - bromo - 1,2 - dimethylcyclohexane}}\] and \[{\rm{(1R,2S)}}\,{\rm{1 - bromo - 1,2 - dimethylcyclohexane}}\]
Note:
In the presence of peroxide, the mechanism of alkene with hydrogen bromide is completed in three steps as chain initiation, chain propagation and then chain termination.
1. In chain initiation, radical is initiated on the most stable carbon.
2. In chain propagation, radical is propagated
(both the above steps are exothermic reactions only in case of hydrogen bromide.
3. In case of hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride, the above steps are endothermic and hence unfavourable.)
In chain termination, the product is formed.
Complete answer
According to Anti Markovnikov rule or peroxide effect or Kharasch effect, when unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide, the bromide ion will join to the carbon carrying more hydrogen atom while hydrogen ion will go to the other carbon atom.
The two different compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structures are known as constitutional isomers. The different structures may have different stereochemistry or different group attachment.
Now, alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the dark and in the absence of per-oxides gives products according to Markovnikov rule. So, when \[{\rm{1,6}}\]- dimethyl-cyclohexene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the dark and in the absence of per-oxides, the bromide ion will join to the carbon carrying less hydrogen atom while hydrogen ion will go to the other carbon but there is an exception that more substituted carbocations are more stable and undergo rearrangement by \[{\rm{1 - 2}}\] hydrogen shift as-

Therefore, the compounds are \[{\rm{(1R,2R)}}\,{\rm{1 - bromo - 1,2 - dimethylcyclohexane}}\] and \[{\rm{(1R,2S)}}\,{\rm{1 - bromo - 1,2 - dimethylcyclohexane}}\]
Note:
In the presence of peroxide, the mechanism of alkene with hydrogen bromide is completed in three steps as chain initiation, chain propagation and then chain termination.
1. In chain initiation, radical is initiated on the most stable carbon.
2. In chain propagation, radical is propagated
(both the above steps are exothermic reactions only in case of hydrogen bromide.
3. In case of hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride, the above steps are endothermic and hence unfavourable.)
In chain termination, the product is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




