
Two conducting and concentric thin spherical shells of radii $a$ and $b$,\[(b > a)\] have charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_2}$ respectively. Now if the inner shell is earthed then the final charge on this shell will be
(a) $\dfrac{{{q_2}{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$
(b) $\dfrac{{ - {q_2}a}}{b}$
(c) $\dfrac{{({q_1} - {q_2})}}{2}$
(d) $ - \dfrac{{{q_2}b}}{a}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: they have given the two thin conducting and concentric shell of radii $a$ and $b$,\[(b > a)\] now here we have to find the final charge on the given shell if the inner shell is earthed first we have to draw a diagram as per my knowledge it is just like gauss law which one of the fundamental Maxwell's equation which describes the relation of the electric field on a Gaussian surface and the total charge enclosed in it.
Complete step by Step solution:
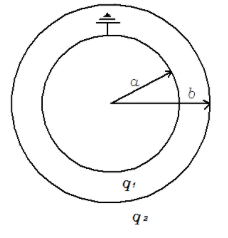
The inner conducting and concentric thin spherical shell is grounded
Therefore the potential $V$ will be $0$
Also the potential at the inner spherical is given by
$V = \dfrac{{K{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{K{Q_2}}}{b}$
In the earlier as we taken the potential $V$ will be $0$ that is $V = 0$ substitute it in the above equation
$0 = \dfrac{{K{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{K{Q_2}}}{b}$
Here in the above equation we can see that $K$ is constant so take it outside
Then the equation can be written as
$0 = K\left( {\dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}} \right)$
Here $K$ is a constant so its value will be $1$then
$0 = \left( {\dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}} \right)$
Now we want the value of ${Q_1}$so take the whole term outside then the equation will be
$ - \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}$
Now we want only the value of ${Q_1}$ so shift $a$ to the R.H.S then we get
$ - {Q_1} = \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Therefore ${Q_1} = - \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Therefore the final charge on this shell ${Q_1} = - \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Hence the correct answer is option (d)
Note:Electric potential is the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from a source point to a particular point against an electric field. Typically, the source point is Earth, although any point beyond the influence of the electric field charge can be used.
Complete step by Step solution:

The inner conducting and concentric thin spherical shell is grounded
Therefore the potential $V$ will be $0$
Also the potential at the inner spherical is given by
$V = \dfrac{{K{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{K{Q_2}}}{b}$
In the earlier as we taken the potential $V$ will be $0$ that is $V = 0$ substitute it in the above equation
$0 = \dfrac{{K{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{K{Q_2}}}{b}$
Here in the above equation we can see that $K$ is constant so take it outside
Then the equation can be written as
$0 = K\left( {\dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}} \right)$
Here $K$ is a constant so its value will be $1$then
$0 = \left( {\dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} + \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}} \right)$
Now we want the value of ${Q_1}$so take the whole term outside then the equation will be
$ - \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{a} = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{b}$
Now we want only the value of ${Q_1}$ so shift $a$ to the R.H.S then we get
$ - {Q_1} = \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Therefore ${Q_1} = - \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Therefore the final charge on this shell ${Q_1} = - \dfrac{{{Q_2}a}}{b}$
Hence the correct answer is option (d)
Note:Electric potential is the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from a source point to a particular point against an electric field. Typically, the source point is Earth, although any point beyond the influence of the electric field charge can be used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




