
Two circles touch each other externally at C and AB is a common tangent to the circles. What is the value of \[\angle ACB\]?
(a). 60°
(b). 45°
(c). 30°
(d). 90°
Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: Construct another common tangent to both the circle at C, which meets AB at P. Consider the triangles ACP, ABP, ABC, and use the fact that the sum of angles of a triangle is 180° to find the angle \[\angle ACB\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
A circle is a round-shaped figure having no corners or edges. It is a closed figure.
The tangent to a circle is a straight line that touches a circle only at one point. The tangent of the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of contact.
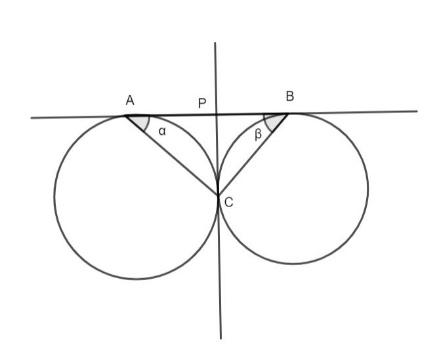
We are given two circles that touch each other at point C and have a common tangent AB.
Draw another common tangent to the circles at point C that meets the tangent AB at P as shown in the figure.
We know that the lengths of the tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal.
Hence, we have PA = PC and PB = PC.
We know that the corresponding angles to the equal sides in a triangle are equal.
In triangle APC, let angle PAC be \[\alpha \]. We have:
\[\angle PCA = \angle PAC = \alpha ..........(1)\]
In triangle BPC, let angle PBC be \[\beta \]. We have:
\[\angle PCB = \angle PBC = \beta ...........(2)\]
Hence, we have:
\[\angle ACB = \angle PCA + \angle PCB\]
\[\angle ACB = \alpha + \beta ............(3)\]
We know that the sum of angles of a triangle is equal to 180°.
In triangle ABC, we have the sum of the three angles as 180°.
\[\angle ACB + \angle BCA + \angle ACB = 180^\circ \]
From equations (1), (2), and (3), we have:
\[(\alpha + \beta ) + \alpha + \beta = 180^\circ \]
Simplifying, we get:
\[2(\alpha + \beta ) = 180^\circ \]
Solving for \[\alpha + \beta \], we get:
\[\alpha + \beta = \dfrac{{180^\circ }}{2}\]
\[\alpha + \beta = 90^\circ \]
From equation (3), we have:
\[\angle ACB = 90^\circ \]
Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Note: You can not assume that the line PC is the angle bisector of C or the point P to be the perpendicular bisector of line AB, these are only the special cases. You need to solve for a general case.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A circle is a round-shaped figure having no corners or edges. It is a closed figure.
The tangent to a circle is a straight line that touches a circle only at one point. The tangent of the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of contact.

We are given two circles that touch each other at point C and have a common tangent AB.
Draw another common tangent to the circles at point C that meets the tangent AB at P as shown in the figure.
We know that the lengths of the tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal.
Hence, we have PA = PC and PB = PC.
We know that the corresponding angles to the equal sides in a triangle are equal.
In triangle APC, let angle PAC be \[\alpha \]. We have:
\[\angle PCA = \angle PAC = \alpha ..........(1)\]
In triangle BPC, let angle PBC be \[\beta \]. We have:
\[\angle PCB = \angle PBC = \beta ...........(2)\]
Hence, we have:
\[\angle ACB = \angle PCA + \angle PCB\]
\[\angle ACB = \alpha + \beta ............(3)\]
We know that the sum of angles of a triangle is equal to 180°.
In triangle ABC, we have the sum of the three angles as 180°.
\[\angle ACB + \angle BCA + \angle ACB = 180^\circ \]
From equations (1), (2), and (3), we have:
\[(\alpha + \beta ) + \alpha + \beta = 180^\circ \]
Simplifying, we get:
\[2(\alpha + \beta ) = 180^\circ \]
Solving for \[\alpha + \beta \], we get:
\[\alpha + \beta = \dfrac{{180^\circ }}{2}\]
\[\alpha + \beta = 90^\circ \]
From equation (3), we have:
\[\angle ACB = 90^\circ \]
Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Note: You can not assume that the line PC is the angle bisector of C or the point P to be the perpendicular bisector of line AB, these are only the special cases. You need to solve for a general case.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




