
Two charges 2μC and −2μC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
(a) Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
(b) What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: Since there are two charges given and both the charges are opposite in nature, this means that the equipotential surface will have the zero potential as both charges are different, they will cancel out the influence of each other. If they are the same charges then the equipotential surface will be the point where the influence from both of them is the same.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that
${{q}_{1}}=2\mu C=2\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
${{q}_{2}}=-2\mu C=-2\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
Distance (r) = 0.06 m
A.) In the first part we need to find the equipotential surface, which means that the potential will be zero at that point due to both the charges
Let “x” be the point in between both the charges where potential is zero
Therefore, by using formula
$\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{x}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{(0.06-x)}]=0$
$\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{x}=-\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{(0.06-x)}$
$\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{x}=\dfrac{-2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{(0.06-x)}$
On solving this, we get
x = 0.03 m
This means that the midpoint of the imaginary straight line passing through both the charges will be the equipotential surface for both the charges. The above illustration, can be diagrammatically shown as below
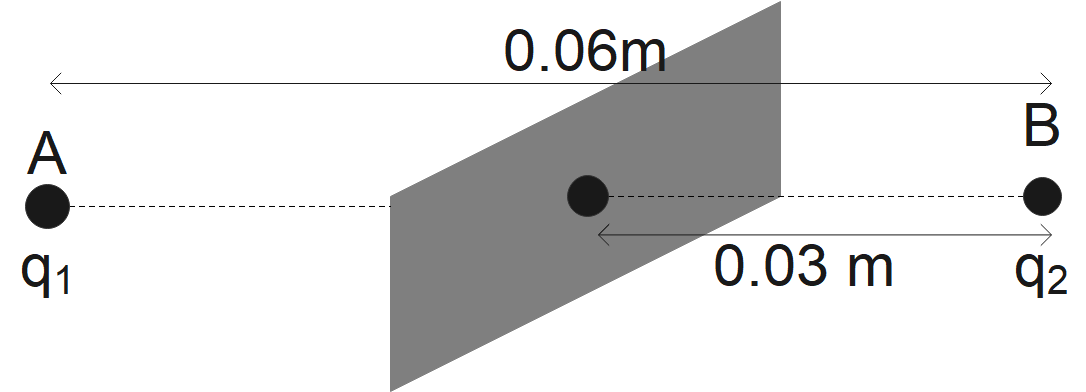
B.) In this part we have been asked about the direction at every point on the surface. Since we all know that the force and field act perpendicular to each other hence, we can say that the electric field will act normal to the plane in the direction of AB as shown in above figure
Note: Since, in the second part we have been asked about the direction of the field and hence, we can say that the potential will be in the direction of the field. Since in the above figure we have found the equipotential surface this means that the field will be in that direction only.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that
${{q}_{1}}=2\mu C=2\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
${{q}_{2}}=-2\mu C=-2\times {{10}^{-6}}C$
Distance (r) = 0.06 m
A.) In the first part we need to find the equipotential surface, which means that the potential will be zero at that point due to both the charges
Let “x” be the point in between both the charges where potential is zero
Therefore, by using formula
$\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}[\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{x}+\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{(0.06-x)}]=0$
$\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}}{x}=-\dfrac{{{q}_{2}}}{(0.06-x)}$
$\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{x}=\dfrac{-2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{(0.06-x)}$
On solving this, we get
x = 0.03 m
This means that the midpoint of the imaginary straight line passing through both the charges will be the equipotential surface for both the charges. The above illustration, can be diagrammatically shown as below

B.) In this part we have been asked about the direction at every point on the surface. Since we all know that the force and field act perpendicular to each other hence, we can say that the electric field will act normal to the plane in the direction of AB as shown in above figure
Note: Since, in the second part we have been asked about the direction of the field and hence, we can say that the potential will be in the direction of the field. Since in the above figure we have found the equipotential surface this means that the field will be in that direction only.
Watch videos on
Two charges 2μC and −2μC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
(a) Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
(b) What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
(a) Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
(b) What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?

Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Physics - NCERT EXERCISE 2.3 | Vishal Kumar Sir
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
489 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
