
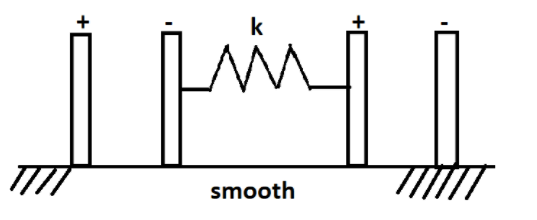
Two charged capacitors have their outer plates fixed and inner plates connected by a spring of force constant \[k\]. The charge on each capacitor is \[q.\] Find the extension in the spring at equilibrium.
A. \[\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{2A{\varepsilon _0}k}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{4A{\varepsilon _0}k}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{A{\varepsilon _0}k}}\]
D. Zero

Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem we need to first use the force between the two parallel plate capacitors and then we need to substitute the formula for the electric field between the plates. The next step is to use Hooke’s law and substitute the force constant given in the question and then equate both the equations to find the extension in the string at equilibrium.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that charge on each capacitor is \[q\]and the plates connected by a spring of force constant \[k\]
The force between the parallel plate capacitors that attract each other is given by,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}qE\]
Here \[q\] is the charge present on the capacitor.
\[E\] is the electric field between the plates.
The electric field between the plates is given by,
\[E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Substituting this in the force equation, we get,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}q\dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Multiplying and dividing by \[A\] , we get
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}q\dfrac{{\sigma A}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}\]
But we know that \[q = \sigma A\]
Therefore substituting the above equation becomes,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}\] ……….. (1)
Let us assume that the spring is elongated by a distance of \[x\].
Hooke’s law can be stated as that the strain present in a solid is directly proportional to the applied stress in the solid within the elastic limit of that solid.
By Hooke’s law, we know that,
\[F = kx\] ……… (2)
Equating equations (1) and (2) we get
Therefore the spring elongated by the distance given by,\[\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}} = kx\]
Note:
The physical origin of the factor \[\dfrac{1}{2}\], in the force between the parallel plate capacitor formula, lies in the fact that just outside the conductor, the field is $E$ , and inside it is zero. Hence, it is the average value,\[E/2\] of the field that contributes to the force.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that charge on each capacitor is \[q\]and the plates connected by a spring of force constant \[k\]
The force between the parallel plate capacitors that attract each other is given by,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}qE\]
Here \[q\] is the charge present on the capacitor.
\[E\] is the electric field between the plates.
The electric field between the plates is given by,
\[E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Substituting this in the force equation, we get,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}q\dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Multiplying and dividing by \[A\] , we get
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}q\dfrac{{\sigma A}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}\]
But we know that \[q = \sigma A\]
Therefore substituting the above equation becomes,
\[F = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}\] ……….. (1)
Let us assume that the spring is elongated by a distance of \[x\].
Hooke’s law can be stated as that the strain present in a solid is directly proportional to the applied stress in the solid within the elastic limit of that solid.
By Hooke’s law, we know that,
\[F = kx\] ……… (2)
Equating equations (1) and (2) we get
Therefore the spring elongated by the distance given by,\[\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}} = kx\]
Note:
The physical origin of the factor \[\dfrac{1}{2}\], in the force between the parallel plate capacitor formula, lies in the fact that just outside the conductor, the field is $E$ , and inside it is zero. Hence, it is the average value,\[E/2\] of the field that contributes to the force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




