
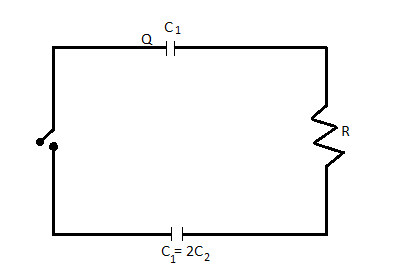
Two capacitors \[{C_1}\] and ${C_2} = 2{C_1}$ are connected in a circuit with a switch between them as shown in the figure. Initially the switch is open and ${C_1}$ holds charge $Q$ . The switch is closed. At steady state, the charge on the each capacitor will be:
(A) $Q,2Q$
(B) $\dfrac{Q}{3},\dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$
(C) $\dfrac{{3Q}}{2},3Q$
(D) $\dfrac{{2Q}}{3},\dfrac{{4Q}}{3}$

Answer
549.3k+ views
Hint: For finding the charges on each plate of capacitor, first we find the common voltage of the circuit. After getting common voltage, we calculate charge on each plate of capacitor using the relationship between capacitance, voltage and charge.
Useful formula:
Relationship between voltage, capacitance and charge is given by the following formula:
$ \Rightarrow Q = CV$
Where, $Q$ is charged, $C$ is capacitance and $V$ is voltage of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that capacitor ${C_1}$ , ${C_2}$ , resistance $R$ and a switch in the circuit in the figure. Initially the switch is open and the capacitor ${C_1}$holds $Q$ charge. When the switch is closed. At steady state, the charge distributed on each plate but voltage across the circuit is the same.
We know that charge is equal to the product of capacitance and voltage.
$ \Rightarrow Q = CV$
So, Voltage can be written as from the above formula
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{C}$
Common voltage can be calculated putting the value of total charge and total capacitance on above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
We know that ${C_2} = 2{C_1}$ , putting this value on above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{{C_1} + 2{C_1}}}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{3{C_1}}}$ $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Let charge on plate of capacitor ${C_1}$ is ${Q_1}$ and charge on plate of capacitor ${C_2}$ is ${Q_2}$ , then total charge $Q$ will be equal to sum of charge ${Q_1}$and ${Q_2}$ .
$ \Rightarrow Q = {Q_1} + {Q_2} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Now, Charge ${Q_1}$ is calculated using the formula,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = {C_1} \times V$
Putting value of voltage $V$ from the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ on the above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = {C_1} \times \dfrac{Q}{{3{C_1}}}$
After simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = \dfrac{Q}{3}$
Putting value of ${Q_1}$ in the equation $\left( 2 \right)$ then we get,
$ \Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{Q}{3} + {Q_2}$
Take $\dfrac{Q}{3}$ into other side to get value of ${Q_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = Q - \dfrac{Q}{3}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$
Therefore, Charge on plate of capacitor ${C_1}$ is $\dfrac{Q}{3}$ and charge on plate of capacitor ${C_2}$ is $\dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$ .
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Charge is measured in Coulomb, voltage is measured in volt, resistance is measured in Ohm, and capacitance is measured in faraday.
Useful formula:
Relationship between voltage, capacitance and charge is given by the following formula:
$ \Rightarrow Q = CV$
Where, $Q$ is charged, $C$ is capacitance and $V$ is voltage of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that capacitor ${C_1}$ , ${C_2}$ , resistance $R$ and a switch in the circuit in the figure. Initially the switch is open and the capacitor ${C_1}$holds $Q$ charge. When the switch is closed. At steady state, the charge distributed on each plate but voltage across the circuit is the same.
We know that charge is equal to the product of capacitance and voltage.
$ \Rightarrow Q = CV$
So, Voltage can be written as from the above formula
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{C}$
Common voltage can be calculated putting the value of total charge and total capacitance on above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
We know that ${C_2} = 2{C_1}$ , putting this value on above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{{C_1} + 2{C_1}}}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{Q}{{3{C_1}}}$ $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Let charge on plate of capacitor ${C_1}$ is ${Q_1}$ and charge on plate of capacitor ${C_2}$ is ${Q_2}$ , then total charge $Q$ will be equal to sum of charge ${Q_1}$and ${Q_2}$ .
$ \Rightarrow Q = {Q_1} + {Q_2} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Now, Charge ${Q_1}$ is calculated using the formula,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = {C_1} \times V$
Putting value of voltage $V$ from the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ on the above formula and we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = {C_1} \times \dfrac{Q}{{3{C_1}}}$
After simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_1} = \dfrac{Q}{3}$
Putting value of ${Q_1}$ in the equation $\left( 2 \right)$ then we get,
$ \Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{Q}{3} + {Q_2}$
Take $\dfrac{Q}{3}$ into other side to get value of ${Q_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = Q - \dfrac{Q}{3}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$
Therefore, Charge on plate of capacitor ${C_1}$ is $\dfrac{Q}{3}$ and charge on plate of capacitor ${C_2}$ is $\dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$ .
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Charge is measured in Coulomb, voltage is measured in volt, resistance is measured in Ohm, and capacitance is measured in faraday.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




