
Two bodies are projected with the same velocity. One body is projected at an angle of $30^{\circ}$ and the other at an angle of $60^{\circ}$ to the horizontal. The ratio of the maximum heights reached is
A. \[3:1\]
B. \[1:3\]
C. \[1:2\]
D. \[2:1\]
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: A body when projected at an inclination from the ground, it is said to experience projectile motion. Then the path followed by the body is called the ballistic trajectory, which is a curved parabolic path. Here, we have to find the ratio between the maximum heights, when the angle of inclination is varied.
Formula used:
$H=\dfrac{u^2sin^2\theta}{2g}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let $u$ be the initial velocity of the body which is projected at an angle $\theta$ from the horizontal. Then the initial velocity $u$ can be resolved into two components along the x and y axis respectively .Let $H$ and $R$ be the maximum distances along the x and y-axis respectively, during the time of flight $T$.Consider the figure as shown below:
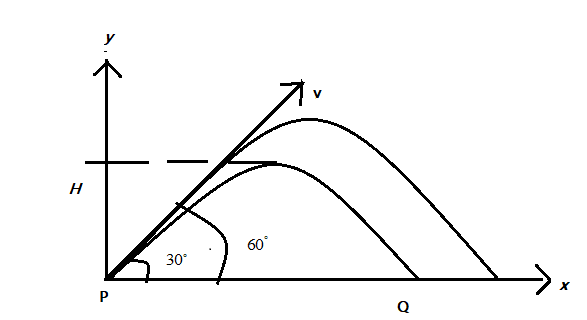
We know from projectile motion that the maximum height $H$ attained by an object which is inclined by some angle $\theta$ is given as $H=\dfrac{u^2sin^2\theta}{2g}$
Here, we have two angles, $\theta_1=30^{\circ}$ and $\theta_2=60^{\circ}$. Let, $H_1$ be the height due to $\theta_1$ and $H_2$ be the height due to $\theta_2$, then taking the ratio of the heights we have,
$\dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{u^2sin^230}{2g}\right)}{\left(\dfrac{u^2sin^260}{2g}\right)}$
Since both the inclination have the same initial velocity, we get
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{sin^230}{sin^260}$
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}}\right)^2}$
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{1}{3}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: When the object is on the air, the only force acting on the body is the force due to gravitation, which pulls the object back to the surface at the speed of acceleration due to gravity. Note that the height of the projected body doesn’t depend on the mass of the body. Here, however we are using the equation of trajectory of the projectile to solve the problem.
Formula used:
$H=\dfrac{u^2sin^2\theta}{2g}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let $u$ be the initial velocity of the body which is projected at an angle $\theta$ from the horizontal. Then the initial velocity $u$ can be resolved into two components along the x and y axis respectively .Let $H$ and $R$ be the maximum distances along the x and y-axis respectively, during the time of flight $T$.Consider the figure as shown below:

We know from projectile motion that the maximum height $H$ attained by an object which is inclined by some angle $\theta$ is given as $H=\dfrac{u^2sin^2\theta}{2g}$
Here, we have two angles, $\theta_1=30^{\circ}$ and $\theta_2=60^{\circ}$. Let, $H_1$ be the height due to $\theta_1$ and $H_2$ be the height due to $\theta_2$, then taking the ratio of the heights we have,
$\dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{u^2sin^230}{2g}\right)}{\left(\dfrac{u^2sin^260}{2g}\right)}$
Since both the inclination have the same initial velocity, we get
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{sin^230}{sin^260}$
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}}\right)^2}$
$\implies \dfrac{H_1}{H_2}=\dfrac{1}{3}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: When the object is on the air, the only force acting on the body is the force due to gravitation, which pulls the object back to the surface at the speed of acceleration due to gravity. Note that the height of the projected body doesn’t depend on the mass of the body. Here, however we are using the equation of trajectory of the projectile to solve the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




