
Two blocks of masses ${M_1} = 4kg$ and ${M_2} = 6kg$ are connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in the figure below. The coefficient of friction between the block ${M_1}$ and the horizontal surface is 0.4. When the system is released the masses ${M_1}$ and \[{M_2}\] start accelerating. What additional mass $m$ should be placed over M so that the masses (${M_1}$ + $m$) slide with a uniform speed?
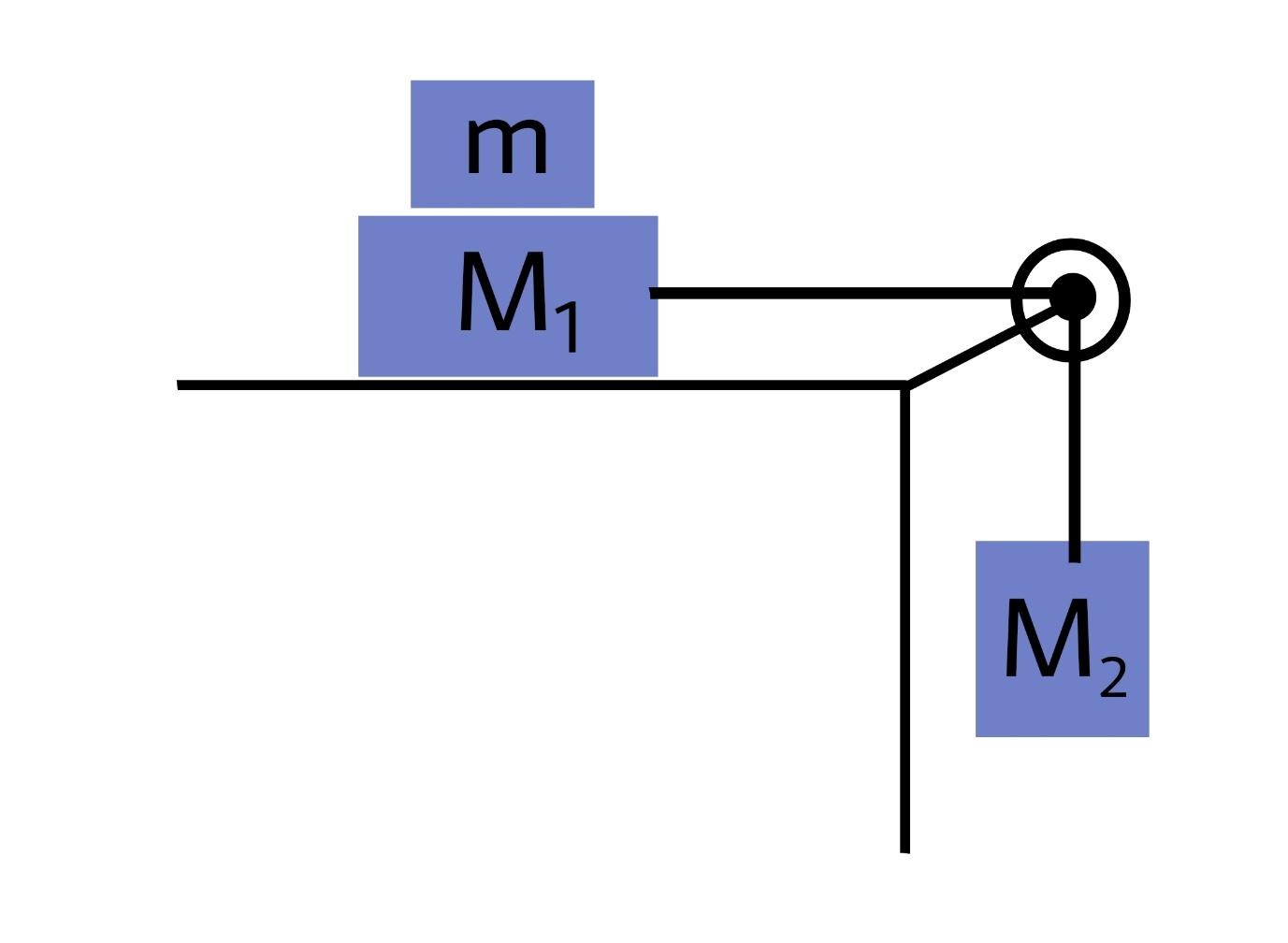
(A) 12kgs
(B) 11khs
(C) 10kgs
(D) 9kgs

Answer
460.8k+ views
Hint: In this question we are asked to find out the mass of the unknown weight $m$ such that the masses (${M_1}$ + $m$) slide with a uniform speed. Now in case of uniform velocity the net force should be balanced or the sum of the net forces on the masses (${M_1}$ + $m$) should be equal to zero.
Complete answer:
Now at first let's draw the free body diagram of the two bodies (${M_1}$ + $m$).
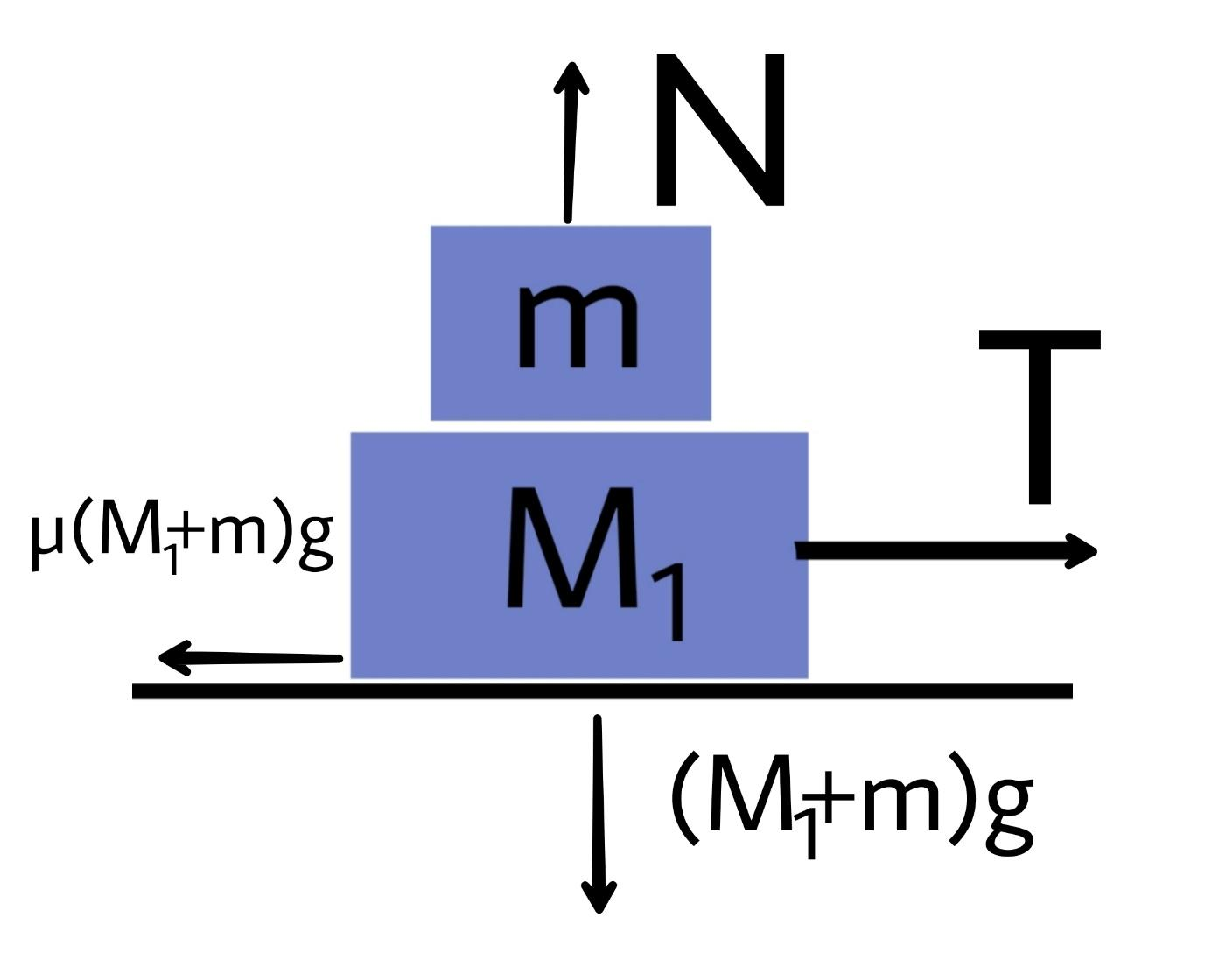
Here the y component of force balances each other so the weight becomes equal to the normal.
$\left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = N$
Since the masses move at a uniform speed the tension force balances the friction force.
$\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = T$ equation 1
Now in this second diagram we analyze the mass.
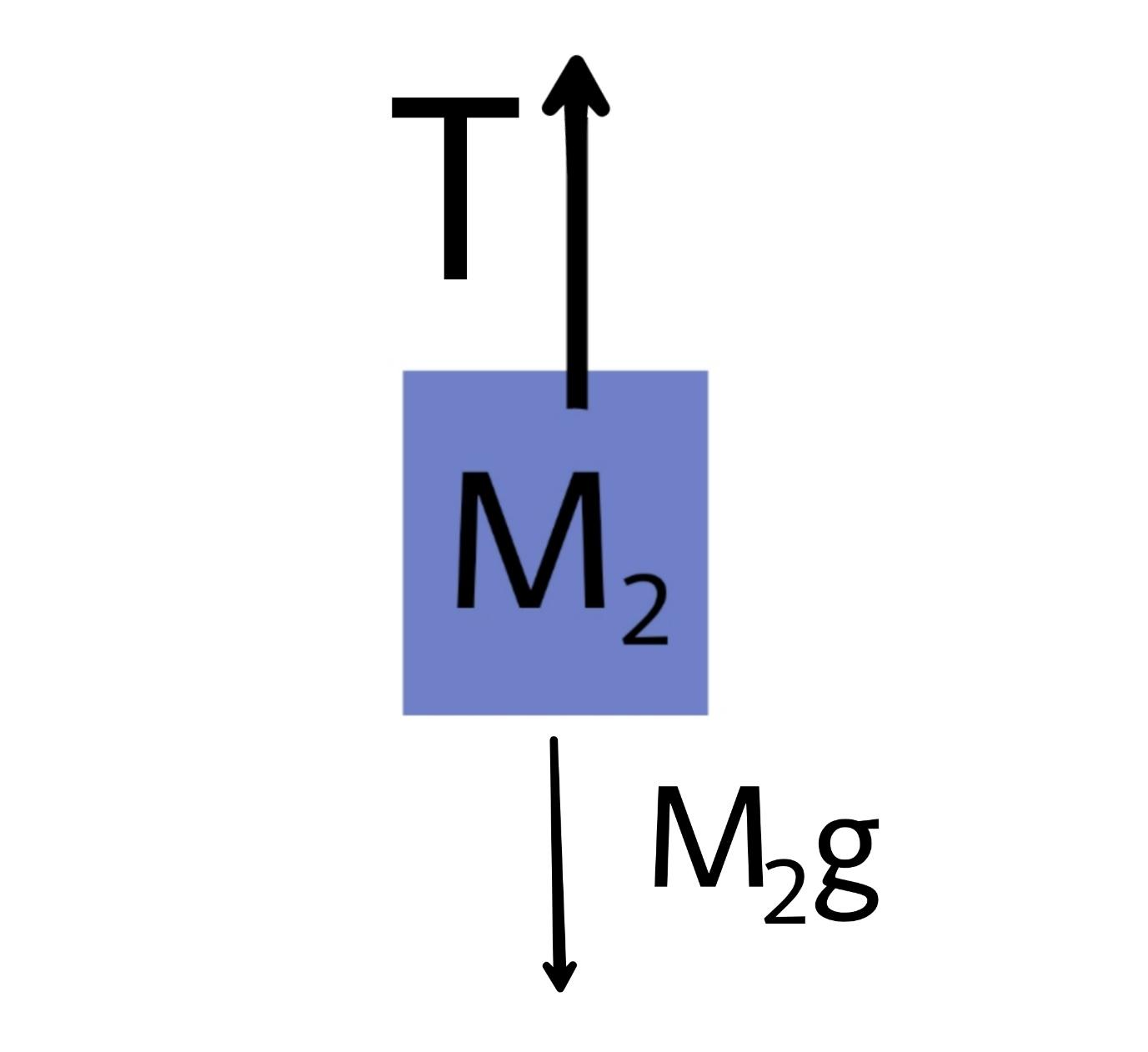
Since the motion is a uniform speed motion the net force on \[{M_2}\] becomes zero so the tension force balances the weight of \[{M_2}\]
$T = {M_2}g$ equation 2
Thus, from equation 1 and 2 we get
\[\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = {M_2}g \]
\[\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right) = {M_2} \]
\[ m = \dfrac{{{M_2}}}{\mu } - {M_1} \]
Now let’s substitute the values.
$m = \dfrac{6}{{0.4}} - 4 = 15 - 4 = 11kgs$
So, the mass of the unknown object is m = 11kgs
The correct option is (B).
Note:
In every case of whether the object is at rest or it is in motion the net force that is acting on the object should be equal to zero, we can also See this from Newton's second law of motion. Here in this question the friction between the ropes and the pulley is ignored. But if there was friction present in the pulley then the rotational motion of the pulley was also to be considered in solving the problem.
Complete answer:
Now at first let's draw the free body diagram of the two bodies (${M_1}$ + $m$).

Here the y component of force balances each other so the weight becomes equal to the normal.
$\left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = N$
Since the masses move at a uniform speed the tension force balances the friction force.
$\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = T$ equation 1
Now in this second diagram we analyze the mass.

Since the motion is a uniform speed motion the net force on \[{M_2}\] becomes zero so the tension force balances the weight of \[{M_2}\]
$T = {M_2}g$ equation 2
Thus, from equation 1 and 2 we get
\[\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right)g = {M_2}g \]
\[\mu \left( {{M_1} + m} \right) = {M_2} \]
\[ m = \dfrac{{{M_2}}}{\mu } - {M_1} \]
Now let’s substitute the values.
$m = \dfrac{6}{{0.4}} - 4 = 15 - 4 = 11kgs$
So, the mass of the unknown object is m = 11kgs
The correct option is (B).
Note:
In every case of whether the object is at rest or it is in motion the net force that is acting on the object should be equal to zero, we can also See this from Newton's second law of motion. Here in this question the friction between the ropes and the pulley is ignored. But if there was friction present in the pulley then the rotational motion of the pulley was also to be considered in solving the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




