
Two blocks of masses $4{\text{ }}kg$ and $2{\text{ }}kg$ are attached to ends of a light spring having spring constant $1200{\text{ }}\dfrac{N}{m}$. The whole system is placed on the smooth horizontal surface. When the spring is in a relaxed state, the $4{\text{ }}kg$ block is given velocity as shown below..."?"
The maximum extension in the spring is?
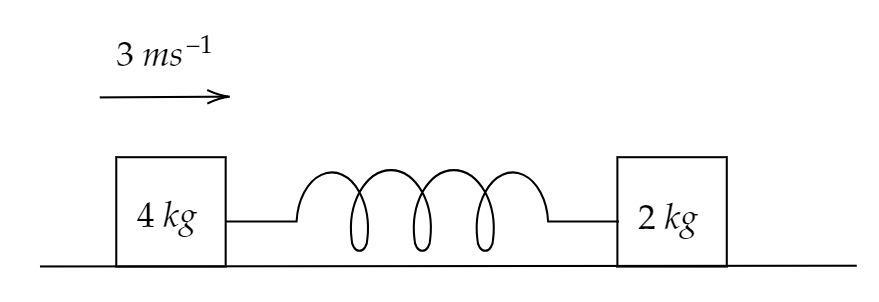
1. $10{\text{ }}cm$
2. $12{\text{ }}cm$
3. $20{\text{ }}cm$
4. $\sqrt {10} {\text{ }}cm$

Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: In the given we have to make use of the spring constant to find the angular velocity. Then from the relation between angular velocity, spring constant and reduced mass we will find the angular velocity. Then with the help of maximum velocity and angular velocity we will find the maximum extension of the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, the $4{\text{ }}kg$ block is provided with a velocity, and thus it keeps on compressing the spring. From Newton’s Third Law we find that the restoring force from the spring pushes the block.
The restoring force that acts on the block is given as,
$F = - kx$ where $F$ is the force that acts on the spring, $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the distance to which the block moves.
Therefore, the system performs S.H.M.
The velocity given in the question $3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$ is the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M. because on going further the velocity will decrease due to resistive force by the spring.
Let the reduced mass of the system be $m$.
Therefore, $m = 4 \times \dfrac{2}{{4 + 2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}{\text{ }}kg$
The angular velocity, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{k}{m}} $
Substituting the values of the variable we get,
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{1200 \times 3}}{4}} = 30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{rad}}{s}$
Let the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M be $V$.
We get, $V = A\omega $ where $A$ is the maximum amplitude and $\omega $ is the angular velocity.
It is given in the question, $V = 3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$
We get,
$3 = A \times 30$
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{{10}}{\text{ }}m$
The maximum extension of the spring is $A = 0.1{\text{ }}m = 10{\text{ }}cm$
The correct option is 1. $10{\text{ }}cm$.
Note: The velocity given in the question is the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M. because on going further the velocity will decrease due to resistive force by the spring. Maximum amplitude is the maximum extension of the spring in S.H.M.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, the $4{\text{ }}kg$ block is provided with a velocity, and thus it keeps on compressing the spring. From Newton’s Third Law we find that the restoring force from the spring pushes the block.
The restoring force that acts on the block is given as,
$F = - kx$ where $F$ is the force that acts on the spring, $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the distance to which the block moves.
Therefore, the system performs S.H.M.
The velocity given in the question $3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$ is the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M. because on going further the velocity will decrease due to resistive force by the spring.
Let the reduced mass of the system be $m$.
Therefore, $m = 4 \times \dfrac{2}{{4 + 2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}{\text{ }}kg$
The angular velocity, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{k}{m}} $
Substituting the values of the variable we get,
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{1200 \times 3}}{4}} = 30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{rad}}{s}$
Let the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M be $V$.
We get, $V = A\omega $ where $A$ is the maximum amplitude and $\omega $ is the angular velocity.
It is given in the question, $V = 3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$
We get,
$3 = A \times 30$
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{{10}}{\text{ }}m$
The maximum extension of the spring is $A = 0.1{\text{ }}m = 10{\text{ }}cm$
The correct option is 1. $10{\text{ }}cm$.
Note: The velocity given in the question is the maximum velocity attained by the S.H.M. because on going further the velocity will decrease due to resistive force by the spring. Maximum amplitude is the maximum extension of the spring in S.H.M.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




