
Two blocks of masses $ 2kg $ and $ 4kg $ are hanging with the help of a massless string passing over an ideal pulley inside an elevator. The elevator is moving upward with an accelerating $ \dfrac{g}{2} $ . The tension in the string connected between the blocks will be (take $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ )
(A) $ 40N $
(B) $ 60N $
(C) $ 80N $
(D) $ 20N $
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: The force on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum. There is an equal and opposite action for every action. Due to the inertia, the force on the object is having an opposite force In the opposite direction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The frame of reference of the lift’s inside, which is attached to the floor, is moving upwards with an acceleration of $ \dfrac{g}{2} $ . So for applying Newton's laws, we need to add a pseudo force $ \left( { = mass \times \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) $ in the downward direction for each mass. In other words, we can say the effective downwards.
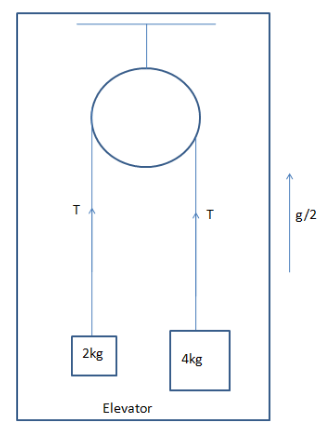
The $ {M_1} $ is the $ 4kg $ mass that is heavier and accelerates downwards. Here, $ {M_2} $ is the $ 2kg $ mass it moves upwards with the equal acceleration of $ {M_1} $ . Let us consider the tight string which has even tension $ T $ throughout the string $ g' = g + \dfrac{g}{2} = \dfrac{{3g}}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - T = 4a $ ………..(1)
$ \Rightarrow T - 2\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) = 2a $ ……….(2)
Here,
$ T - 3g = 2a $
Now rearranging the equation,
$ T = 3g + 2a $
Now solving the equation (1) from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - \left( {3g + 2a} \right) = 4a $
After simplification,
$ a = \dfrac{g}{2} $
Now apply the values in the equation we get
Hence,
$ T = 3g + 2\left( {\dfrac{g}{2}} \right)t $
After solving the equation we get,
$ T = 40N $
Finally, the answer is an option (A).
Note:
There are three laws that will help to describe the relationship between the object's motion and force on an object.
When an object moves from one place to another which is called a motion,
A force that makes an object with a heavy mass can change its velocity; it includes beginning moving from a state of rest.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The frame of reference of the lift’s inside, which is attached to the floor, is moving upwards with an acceleration of $ \dfrac{g}{2} $ . So for applying Newton's laws, we need to add a pseudo force $ \left( { = mass \times \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) $ in the downward direction for each mass. In other words, we can say the effective downwards.

The $ {M_1} $ is the $ 4kg $ mass that is heavier and accelerates downwards. Here, $ {M_2} $ is the $ 2kg $ mass it moves upwards with the equal acceleration of $ {M_1} $ . Let us consider the tight string which has even tension $ T $ throughout the string $ g' = g + \dfrac{g}{2} = \dfrac{{3g}}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - T = 4a $ ………..(1)
$ \Rightarrow T - 2\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) = 2a $ ……….(2)
Here,
$ T - 3g = 2a $
Now rearranging the equation,
$ T = 3g + 2a $
Now solving the equation (1) from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {g + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - \left( {3g + 2a} \right) = 4a $
After simplification,
$ a = \dfrac{g}{2} $
Now apply the values in the equation we get
Hence,
$ T = 3g + 2\left( {\dfrac{g}{2}} \right)t $
After solving the equation we get,
$ T = 40N $
Finally, the answer is an option (A).
Note:
There are three laws that will help to describe the relationship between the object's motion and force on an object.
When an object moves from one place to another which is called a motion,
A force that makes an object with a heavy mass can change its velocity; it includes beginning moving from a state of rest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




