
Two blocks of masses $1kg$ and $2kg$ are connected by a metal wire going over a smooth pulley. The breaking stress of metal is $\dfrac{40}{3\pi }\times {{10}^{6}}N{{m}^{-2}}$ . What should be the minimum radius of wire used if it should not break? $\left( g=10m{{s}^{-2}} \right)$
A. $0.5mm$
B. $1mm$
C.$1.5mm$
D.$2mm$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Tension due to a string
$T=\dfrac{2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}g$
In which ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the mass of the blocks connected to the metal wire.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity as well.
This equation should be used here for solving.
Complete answer:
First of all let us look at what tension means. The tension which is otherwise called as force is the force that is transmitted through a cable, rope, wire or a string when it is pulled tightly by the forces acting from the two opposite ends. It is getting directed along the length of the cable or wire and pulls equally on the objects on the two opposite ends of the wire. Tension is a scalar quantity. A string or rope or a metal wire is sometimes idealized as one dimension, having length. If there is no bend in the string, as occurs with vibrations or pulleys, then tension is a constant along the chord, equal to the magnitude of the forces applied by the ends of the string. These are the similar forces exerted on the ends of the chord by the masses to which the ends are attached.
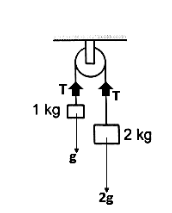
Tension due to a string is found using the free body diagram,
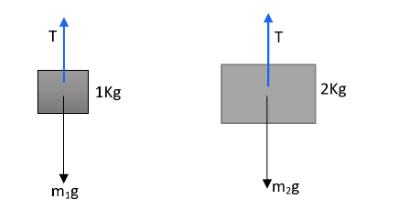
Force acting on ${m}_{1}$ is
${{\text{m}}_{1}}g-T={{m}_{1}}a $
Force acting on ${m}_{2}$ is
$T - m_2 g={{m}_{2}}a$
Using these, we can find the acceleration of the body,
$a=\dfrac{\left( {{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \right)g}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Substituting the value of acceleration in any of the above given equation,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}g-T={{m}_{1}}a \\
& T={{m}_{1}}\left( g-a \right) \\
& T={{m}_{1}}\left( g-\dfrac{\left( {{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \right)g}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore tension is given as,
$T=\dfrac{2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}g$
In which ${{m}_{1}}$and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the mass of the blocks connected to the metal wire.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}\times {{10}^{3}}mm=1mm$
$T=\dfrac{2\times 1\times 2}{1+2}\times 10N$
$T=\dfrac{40}{3}N$
If r is the minimum radius, then breaking stress S is given by
$S=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{40}{3}}{\pi {{r}^{2}}} \right)$
Substituting the value of r in this will give,
$\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{40}{3}}{\pi {{r}^{2}}} \right)=\dfrac{40}{3\pi }\times {{10}^{6}}$
Hence we get like this
${{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{6}}}$
Therefore the minimum radius is
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}m$
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}\times {{10}^{3}}mm=1mm$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The tension which is otherwise called as force is the force that is transmitted through a cable, rope, wire or a string when it is pulled tightly by the forces acting from the two opposite ends. The units of the quantities should be taken care of properly.
$T=\dfrac{2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}g$
In which ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the mass of the blocks connected to the metal wire.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity as well.
This equation should be used here for solving.
Complete answer:
First of all let us look at what tension means. The tension which is otherwise called as force is the force that is transmitted through a cable, rope, wire or a string when it is pulled tightly by the forces acting from the two opposite ends. It is getting directed along the length of the cable or wire and pulls equally on the objects on the two opposite ends of the wire. Tension is a scalar quantity. A string or rope or a metal wire is sometimes idealized as one dimension, having length. If there is no bend in the string, as occurs with vibrations or pulleys, then tension is a constant along the chord, equal to the magnitude of the forces applied by the ends of the string. These are the similar forces exerted on the ends of the chord by the masses to which the ends are attached.

Tension due to a string is found using the free body diagram,

Force acting on ${m}_{1}$ is
${{\text{m}}_{1}}g-T={{m}_{1}}a $
Force acting on ${m}_{2}$ is
$T - m_2 g={{m}_{2}}a$
Using these, we can find the acceleration of the body,
$a=\dfrac{\left( {{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \right)g}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Substituting the value of acceleration in any of the above given equation,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}g-T={{m}_{1}}a \\
& T={{m}_{1}}\left( g-a \right) \\
& T={{m}_{1}}\left( g-\dfrac{\left( {{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \right)g}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore tension is given as,
$T=\dfrac{2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}g$
In which ${{m}_{1}}$and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the mass of the blocks connected to the metal wire.
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}\times {{10}^{3}}mm=1mm$
$T=\dfrac{2\times 1\times 2}{1+2}\times 10N$
$T=\dfrac{40}{3}N$
If r is the minimum radius, then breaking stress S is given by
$S=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{40}{3}}{\pi {{r}^{2}}} \right)$
Substituting the value of r in this will give,
$\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{40}{3}}{\pi {{r}^{2}}} \right)=\dfrac{40}{3\pi }\times {{10}^{6}}$
Hence we get like this
${{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{6}}}$
Therefore the minimum radius is
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}m$
$r=\dfrac{1}{{{10}^{3}}}\times {{10}^{3}}mm=1mm$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The tension which is otherwise called as force is the force that is transmitted through a cable, rope, wire or a string when it is pulled tightly by the forces acting from the two opposite ends. The units of the quantities should be taken care of properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




