
Two blocks of mass capital M and small M are kept on the trolley whose all surfaces are smooth. Select the correct statement.
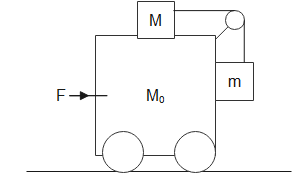
1. If $F = 0$ blocks cannot remain stationary.
2. For one unique value of $F$ , blocks will be stationary.
3. Blocks cannot be stationary for any value of $F$ because all surfaces are smooth
4. Both $1{\text{ and 2}}$ .

Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: For solving questions related to block and wedge, we need to understand how to draw a free body diagram of the bodies provided. In the given diagram we can see there are three bodies with a force $F$ applied on mass ${M_0}$. Thus, we can use Newton's second law of motion to equate the force.
Complete step by step answer:
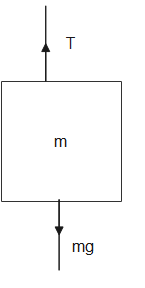
We can see the two masses M and m are connected by a string. Let its tension be T. Let us draw the Free body diagrams of M, m and ${M_0}$.
Now by drawing the free body diagrams, we can see that that tension T equals the weight of m.
Thus $T = mg --(1)$
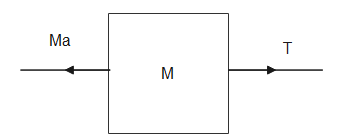
Now let the acceleration of the mass M be a. As the only force experienced by it is T (as the surface is smooth hence no friction), thus we can use Newton's second law of motion to equate the tension T.
Thus $T = Ma --(2)$
Hence from 1 and 2: $a = \dfrac{{mg}}{M} -- (3)$
Now as the applied force on the whole system is F, thus acceleration of system $a'$ will be: $a' = \dfrac{F}{{m + M + {M_0}}}- - - - (4$.
But we see in the question, we have to find when the blocks will move together, thus $a' = a$.
Hence from equation 3 and equation 4 we see:
$F = \dfrac{{mg({M_0} + M + m)}}{M}$ .
Now by checking each of the given options we see that:
Now by seeing the options we see only option 1 is correct.
This is because if $F = 0$, then a' = 0 , but there is an acceleration $a$ which is non zero, thus blocks move.
The second option is correct because there is a value of force for which both accelerations are equal, thus the blocks remain stationary.
Blocks cannot be stationary is a wrong statement because there is a value of force for which they are stationary.
Thus, we see that two options are the correct,
Hence the correct answer is option $4$.
Note: These types of questions are based on the combined application of tension, Newton's laws of motion. Just drawing the free-body diagrams would solve the problem. Remember the important condition that all the bodies move with equal acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
We can see the two masses M and m are connected by a string. Let its tension be T. Let us draw the Free body diagrams of M, m and ${M_0}$.
Now by drawing the free body diagrams, we can see that that tension T equals the weight of m.
Thus $T = mg --(1)$

Now let the acceleration of the mass M be a. As the only force experienced by it is T (as the surface is smooth hence no friction), thus we can use Newton's second law of motion to equate the tension T.
Thus $T = Ma --(2)$

Hence from 1 and 2: $a = \dfrac{{mg}}{M} -- (3)$
Now as the applied force on the whole system is F, thus acceleration of system $a'$ will be: $a' = \dfrac{F}{{m + M + {M_0}}}- - - - (4$.
But we see in the question, we have to find when the blocks will move together, thus $a' = a$.
Hence from equation 3 and equation 4 we see:
$F = \dfrac{{mg({M_0} + M + m)}}{M}$ .
Now by checking each of the given options we see that:
Now by seeing the options we see only option 1 is correct.
This is because if $F = 0$, then a' = 0 , but there is an acceleration $a$ which is non zero, thus blocks move.
The second option is correct because there is a value of force for which both accelerations are equal, thus the blocks remain stationary.
Blocks cannot be stationary is a wrong statement because there is a value of force for which they are stationary.
Thus, we see that two options are the correct,
Hence the correct answer is option $4$.
Note: These types of questions are based on the combined application of tension, Newton's laws of motion. Just drawing the free-body diagrams would solve the problem. Remember the important condition that all the bodies move with equal acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




