
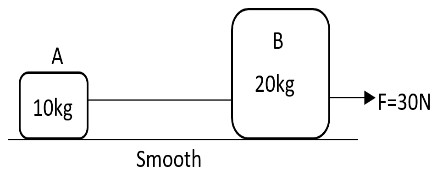
Two blocks A and B are connected by a massless string as represented in the diagram. A force of $30N$ is applied on block B, the distance travelled by centre of mass in $2s$ starting from the rest will be
$\begin{align}
& A.1m \\
& B.2m \\
& C.3m \\
& D.\text{none of these} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: First of all find the total mass of the centre of masses. Draw the free body diagram of the centre of mass of the system. Calculate the force acting on the centre of mass. Using this, find the acceleration of the centre of mass. Then use the second law of motion for calculating the displacement. This all will help you in solving this question.
Complete answer:
First of all, the mass of the block A is given as,
${{m}_{A}}=10kg$
Mass of the block B has been mentioned as,
${{m}_{B}}=20kg$
Time taken has been mentioned as,
$t=2s$
Force acting can be written as,
$F=30N$
Let us assume that the initial velocity on the body be,
$u=0m{{s}^{-1}}$
The total mass on the centre of mass will be,
$M={{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}$
Substituting the values in it,
$\Rightarrow M=10+20=30kg$
The force acting on it will be equivalent to the force acting on the centre of mass. That is,
$\Rightarrow F=30N$
The free body diagram of the centre of mass can be shown as,
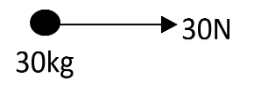
It is to be noted that the internal tension will not affect the centre of mass motion.
The acceleration of the centre of mass is mentioned as,
$a=\dfrac{F}{M}$
Substituting the values in it,
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{30}{30}=1m{{s}^{-2}}$
According to the second equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Substitute the values in it will give,
$\Rightarrow s=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times {{2}^{2}}=2m$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The centre of mass is defined as the position described which is relative to an object or system of bodies. It will be the mean position of all the portions of the system which will be weighted in accordance with their masses. In short the centre of mass is a point where the whole mass of the system is assumed to be concentrated.
Complete answer:
First of all, the mass of the block A is given as,
${{m}_{A}}=10kg$
Mass of the block B has been mentioned as,
${{m}_{B}}=20kg$
Time taken has been mentioned as,
$t=2s$
Force acting can be written as,
$F=30N$
Let us assume that the initial velocity on the body be,
$u=0m{{s}^{-1}}$
The total mass on the centre of mass will be,
$M={{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}$
Substituting the values in it,
$\Rightarrow M=10+20=30kg$
The force acting on it will be equivalent to the force acting on the centre of mass. That is,
$\Rightarrow F=30N$
The free body diagram of the centre of mass can be shown as,

It is to be noted that the internal tension will not affect the centre of mass motion.
The acceleration of the centre of mass is mentioned as,
$a=\dfrac{F}{M}$
Substituting the values in it,
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{30}{30}=1m{{s}^{-2}}$
According to the second equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Substitute the values in it will give,
$\Rightarrow s=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times {{2}^{2}}=2m$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The centre of mass is defined as the position described which is relative to an object or system of bodies. It will be the mean position of all the portions of the system which will be weighted in accordance with their masses. In short the centre of mass is a point where the whole mass of the system is assumed to be concentrated.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




