
Triangle ABC is a right triangle such that $AB=AC$ and bisector of angle $C$ intersects the sides $AB$ at $D$. Prove that $AC+AD=BC$.
Answer
511.5k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been given with a right triangle $\Delta ABC$, for which the length of $AB=AC$ and the triangle is right-angled at $\angle A$. We will solve this question by using the Pythagoras theorem to get the value of the hypotenuse and then use the property of angle bisector theorem to get the ratio of sides. We will then simplify the expression and get the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that $\Delta ABC$ is a right triangle such that $AB=AC$ and there is an angle bisector present at angle $C$ which intersects at the side $AB$ at a point $D$.
We can draw the diagram as:
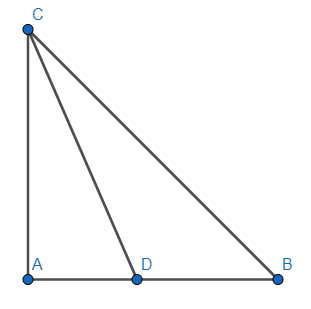
Now in $\Delta ABC$, using Pythagoras theorem, we get:
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
Now we know that $AB=AC$, consider the length be $x$, on substituting, we get:
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
On adding the terms on the left-hand side, we get:
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
On taking the square root on both the sides, we get:
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{2}x=CB$
Now we know the length of $BD$ as:
$\Rightarrow BD=AB-AD$
Let the value of $AD=b$ therefore, we get:
$\Rightarrow BD=a-b$.
Now in the given triangle, by angle bisector theorem, we know that the ratio of the adjacent sides of the bisected angle and the ratio of the line segments formed at the point where the bisector intersects is equal, we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{a-b}=\dfrac{a}{a\sqrt{2}}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{a-b}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
On rearranging the terms, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a}{1+\sqrt{2}}$
On rationalizing the denominator, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a}{1+\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1-\sqrt{2}}{1-\sqrt{2}}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a\left( 1-\sqrt{2} \right)}{1-2}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a\left( 1-\sqrt{2} \right)}{-1}$
On taking the negative sign in the numerator, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=a\left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=a\sqrt{2}-a$
On rearranging, we get:
$\Rightarrow a+b=a\sqrt{2}$
Now we know that $AC=a$, $AD=b$ and $BC=a\sqrt{2}$ therefore, we get:
$\Rightarrow AC+AD=BC$, hence proved.
Note: In this question we have used the Pythagoras theorem followed by the angle bisector theorem to get the required solution. It is to be remembered that when taking the square root on both sides, only the positive root is considered since length cannot be negative. To solve these types of questions, diagrams should be made for simplification.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that $\Delta ABC$ is a right triangle such that $AB=AC$ and there is an angle bisector present at angle $C$ which intersects at the side $AB$ at a point $D$.
We can draw the diagram as:

Now in $\Delta ABC$, using Pythagoras theorem, we get:
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
Now we know that $AB=AC$, consider the length be $x$, on substituting, we get:
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
On adding the terms on the left-hand side, we get:
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=C{{B}^{2}}$
On taking the square root on both the sides, we get:
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{2}x=CB$
Now we know the length of $BD$ as:
$\Rightarrow BD=AB-AD$
Let the value of $AD=b$ therefore, we get:
$\Rightarrow BD=a-b$.
Now in the given triangle, by angle bisector theorem, we know that the ratio of the adjacent sides of the bisected angle and the ratio of the line segments formed at the point where the bisector intersects is equal, we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{a-b}=\dfrac{a}{a\sqrt{2}}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{a-b}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
On rearranging the terms, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a}{1+\sqrt{2}}$
On rationalizing the denominator, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a}{1+\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1-\sqrt{2}}{1-\sqrt{2}}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a\left( 1-\sqrt{2} \right)}{1-2}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a\left( 1-\sqrt{2} \right)}{-1}$
On taking the negative sign in the numerator, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=a\left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow b=a\sqrt{2}-a$
On rearranging, we get:
$\Rightarrow a+b=a\sqrt{2}$
Now we know that $AC=a$, $AD=b$ and $BC=a\sqrt{2}$ therefore, we get:
$\Rightarrow AC+AD=BC$, hence proved.
Note: In this question we have used the Pythagoras theorem followed by the angle bisector theorem to get the required solution. It is to be remembered that when taking the square root on both sides, only the positive root is considered since length cannot be negative. To solve these types of questions, diagrams should be made for simplification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




