
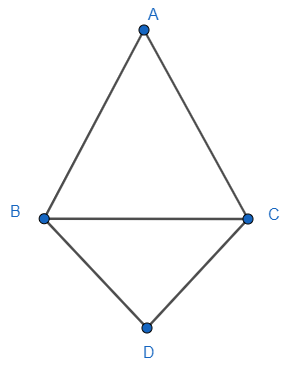
Triangle ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC. Show that $\angle ABD=\angle ACD$.

Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: We first consider the theorem of equality of angles for isosceles triangle where angles opposite to the equal sides of an isosceles triangle are also equal. We consider the $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta DBC$ to find their equal angles. Then we add them to prove the given relation.
Complete step by step answer:
$\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta DBC$ are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC.
We know that the angles opposite to the equal sides of an isosceles triangle is also equal.
For $\Delta ABC$, the sides AB and AC are equal. The opposite angles of those sides are $\angle ABC$ and $\angle ACB$ respectively. Therefore, $\angle ABC=\angle ACB$.
For $\Delta DBC$, the sides DB and DC are equal. The opposite angles of those sides are $\angle DBC$ and $\angle DCB$ respectively. Therefore, $\angle DBC=\angle DCB$.
We got two equations of equality of angles.
We add them and get $\angle ABC+\angle DBC=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$.
Looking at the image we can say that the angles $\angle ABD$ and $\angle ACD$ can be broken into two parts.
We have $\angle ABD=\angle ABC+\angle DBC$ and $\angle ACD=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$.
We know that $\angle ABC+\angle DBC=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$ which gives that $\angle ABD=\angle ACD$.
Thus proved $\angle ABD=\angle ACD$.
Note: We need to be careful about adding wrong angles with one another. In addition if we had added $\angle ABC+\angle DCB$, then we wouldn’t have gotten neither $\angle ABD$ nor $\angle ACD$. Similar things can be said for $\angle DBC+\angle ACB$.
Complete step by step answer:
$\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta DBC$ are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC.
We know that the angles opposite to the equal sides of an isosceles triangle is also equal.
For $\Delta ABC$, the sides AB and AC are equal. The opposite angles of those sides are $\angle ABC$ and $\angle ACB$ respectively. Therefore, $\angle ABC=\angle ACB$.
For $\Delta DBC$, the sides DB and DC are equal. The opposite angles of those sides are $\angle DBC$ and $\angle DCB$ respectively. Therefore, $\angle DBC=\angle DCB$.
We got two equations of equality of angles.
We add them and get $\angle ABC+\angle DBC=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$.
Looking at the image we can say that the angles $\angle ABD$ and $\angle ACD$ can be broken into two parts.
We have $\angle ABD=\angle ABC+\angle DBC$ and $\angle ACD=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$.
We know that $\angle ABC+\angle DBC=\angle ACB+\angle DCB$ which gives that $\angle ABD=\angle ACD$.
Thus proved $\angle ABD=\angle ACD$.
Note: We need to be careful about adding wrong angles with one another. In addition if we had added $\angle ABC+\angle DCB$, then we wouldn’t have gotten neither $\angle ABD$ nor $\angle ACD$. Similar things can be said for $\angle DBC+\angle ACB$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




