
To what height should a cylindrical vessel be filled with a homogenous liquid to make the force with which the liquid pressure on the sides of the vessel equal to the force exerted by liquid on the bottom of the vessel?
[A] Equal to the radius
[B] Less than radius
[C] More than radius
[D] Four times of radius
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand buoyancy force and the pressure exerted by liquid. Whenever any object is pressed inside water then it replaces liquid around it, so water exerts an upward force on the object, this force is known as buoyant force. Pressure exerted by liquid is mathematically defined as the product of density of liquid, acceleration due to gravity and height of the water column above it.
Complete answer:
Let the radius of cylindrical vessel be, $ r $ and height of liquid to be filled is $ h $
Also let the density of water be $ \rho $
So. The mass of water is defined as, $ M = \rho V $
Here, V is volume of water
We know volume of water in form of cylindrical vessel is, $ V = \pi {r^2}h $
So the mass is, $ M = \pi \rho {r^2}h $
So the force exerted on bottom of vessel is, $ W = Mg $
Putting values we get, $ W = \pi \rho {r^2}gh \to (i) $
Let $ dx $ be elemental length of water at distance of $ x $ from above, as shown in figure
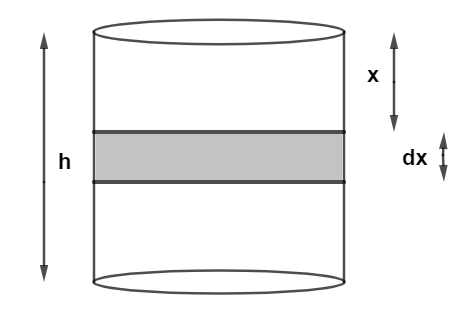
So the pressure exerted by liquid on side of vessel would be, $ P = \rho gx $
Let the elemental area be $ dA $ and it is equal to, $ dA = 2\pi rdx $
So, elemental force exerted by water on side of vessel is, $ dF = PdA $
Putting values we get, $ dF = (\rho gx)(2\pi rdx) $
$ dF = 2\pi \rho rgxdx $
Integrating we get, $ F = 2\pi \rho rg{\int_0^h {xdx} ^2} $
$ F = 2\pi \rho rg{\left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \right]^h}_0 $
$ F = \pi \rho rgh $
So now we equate both the force on sides of vessel and due to liquid column on bottom of vessel, $ W = F $
Putting values we get, $ \pi \rho {r^2}hg = \pi \rho r{h^2}g $
$ h = r $
So the correct option is, [A] Equal to the radius.
Note:
It should be remembered that, here we assumed that the liquid is of uniform density. Also the limit on “x” is from $ 0 $ to h. Also here we have used the elemental concept because we need to find what is the force exerted by whole water at the side of a vessel, so we calculated the elemental force due to one column and then later integrated it for the whole water vessel.
Complete answer:
Let the radius of cylindrical vessel be, $ r $ and height of liquid to be filled is $ h $
Also let the density of water be $ \rho $
So. The mass of water is defined as, $ M = \rho V $
Here, V is volume of water
We know volume of water in form of cylindrical vessel is, $ V = \pi {r^2}h $
So the mass is, $ M = \pi \rho {r^2}h $
So the force exerted on bottom of vessel is, $ W = Mg $
Putting values we get, $ W = \pi \rho {r^2}gh \to (i) $
Let $ dx $ be elemental length of water at distance of $ x $ from above, as shown in figure

So the pressure exerted by liquid on side of vessel would be, $ P = \rho gx $
Let the elemental area be $ dA $ and it is equal to, $ dA = 2\pi rdx $
So, elemental force exerted by water on side of vessel is, $ dF = PdA $
Putting values we get, $ dF = (\rho gx)(2\pi rdx) $
$ dF = 2\pi \rho rgxdx $
Integrating we get, $ F = 2\pi \rho rg{\int_0^h {xdx} ^2} $
$ F = 2\pi \rho rg{\left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \right]^h}_0 $
$ F = \pi \rho rgh $
So now we equate both the force on sides of vessel and due to liquid column on bottom of vessel, $ W = F $
Putting values we get, $ \pi \rho {r^2}hg = \pi \rho r{h^2}g $
$ h = r $
So the correct option is, [A] Equal to the radius.
Note:
It should be remembered that, here we assumed that the liquid is of uniform density. Also the limit on “x” is from $ 0 $ to h. Also here we have used the elemental concept because we need to find what is the force exerted by whole water at the side of a vessel, so we calculated the elemental force due to one column and then later integrated it for the whole water vessel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




