
To have an earth synchronous satellite it should be launched at the proper height moving from
(A) North to South in a polar plane
(B) East to West in an equatorial plane
(C) South to North in a polar plane
(D) West to East in an equatorial plane
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:In order to answer this question, we must have knowledge about the direction of revolution of earth and meaning of synchronous.
Complete step by step answer:
Geosynchronous satellites revolve in the geosynchronous orbit with an orbital period that is equal to the Earth's rotational period. These satellites take 1day to complete one rotation around the earth. However, the orbital plane for a typical geosynchronous satellite is generally not in the equatorial plane. When a geosynchronous satellite is placed directly above the Equator with a circular orbit and angular velocity which are the same as that of the Earth, the satellite is known as a geostationary satellite. These satellites appear to be stationary above a certain point due to the synchronization.
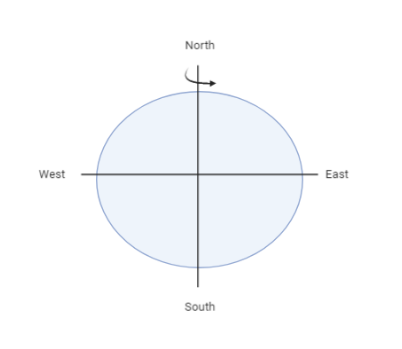
Rotation of earth from west to east.Since these satellites are moving at the same speed and direction of earth that is west to east these satellites are stationary. Synchronous to earth means the same as earth with respect to rotation about its axis and velocity. For the satellite to be 'synchronous' with the Earth, its period of revolution should be equal to Earth's rotation. For this, the satellite has to revolve along the direction of Earth's rotation that is from West to East.
Note: Sometimes students get confused in between the geostationary and geosynchronous orbits, so always remember the difference between them that geostationary orbits fall in the same category as geosynchronous orbits, but it’s parked over the equator. This one special quality makes it unique from geosynchronous orbits.
Complete step by step answer:
Geosynchronous satellites revolve in the geosynchronous orbit with an orbital period that is equal to the Earth's rotational period. These satellites take 1day to complete one rotation around the earth. However, the orbital plane for a typical geosynchronous satellite is generally not in the equatorial plane. When a geosynchronous satellite is placed directly above the Equator with a circular orbit and angular velocity which are the same as that of the Earth, the satellite is known as a geostationary satellite. These satellites appear to be stationary above a certain point due to the synchronization.

Rotation of earth from west to east.Since these satellites are moving at the same speed and direction of earth that is west to east these satellites are stationary. Synchronous to earth means the same as earth with respect to rotation about its axis and velocity. For the satellite to be 'synchronous' with the Earth, its period of revolution should be equal to Earth's rotation. For this, the satellite has to revolve along the direction of Earth's rotation that is from West to East.
Note: Sometimes students get confused in between the geostationary and geosynchronous orbits, so always remember the difference between them that geostationary orbits fall in the same category as geosynchronous orbits, but it’s parked over the equator. This one special quality makes it unique from geosynchronous orbits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




