
To get output ‘1’ at R, for the given logic gate circuit the input values must be
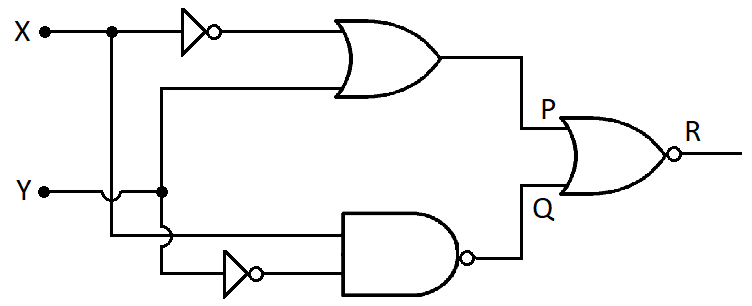
(A) X = 0, Y = 1
(B) X = 1, Y = 1
(C) X = 0, Y = 0
(D) X = 1, Y = 0

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint
To find the output at the point R we first need to find the solution at R in the terms of the input variables X and Y. After that from the solution we need to find the values of X and Y for which the output will be 1.
Formula Used: In this solution we have used the following formula,
$\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$ and
$A \cdot A = A$
Complete step by step answer
Let us first redraw the diagram and give names to the various points.
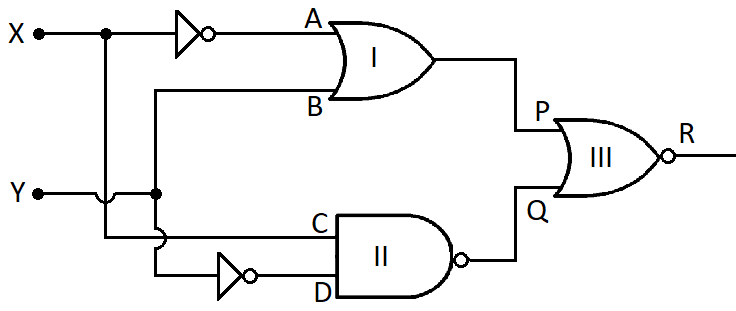
Now, for the OR gate named I, the inputs are A and B. The value of A is given as, $A = \bar X$. And the value of B is Y. The output of this gate will be,
$P = A + B$,
Substituting we get,
$P = \bar X + Y$
Now gate II is an NAND gate. The inputs of this gate are named as C and D. We have the input C as X and the input D as, $D = \bar Y$
The output of an AND gate is given as, $CD$ and for a NAND gate the output will be,
$Q = \overline {C \cdot D} $
Substituting we get,
$Q = \overline {X \cdot \bar Y} $
Now the gate III is a NOR gate. The inputs of this gate are P and Q. So the output R will be,
$R = \overline {P + Q} $
Substituting the values of P and Q we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right) + \overline {X \cdot \bar Y} } $
So we can simplify this from the formula, $\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$
Therefore we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right)} \cdot \overline {\overline {X \cdot \bar Y} } $
Hence we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right)} \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now in the first part we can use the formula, $\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$ again and get,
$R = \left( {\bar{ \bar X} \cdot \bar Y} \right) \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Hence we have,
$R = \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right) \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now since $A \cdot A = A$, so we get
$R = \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now for the output R to be 1, both X and $\bar Y$ has to be 1
So the value of X is 1 and $\bar Y$ is 1. So Y is 0.
Hence X has to be 1 and Y has to be 0
Therefore the correct option is (D).
Note
A digital logic gate is an electronic circuit which makes logical decisions based on the combination of inputs. There are three basic types of logic gates, namely AND gate, OR gate and NOT gate. For the AND gate the output 1 only when both the inputs are 1. For the OR gate, the output is 1 when any one of the inputs are 1 and the NOT gate reverses the input.
To find the output at the point R we first need to find the solution at R in the terms of the input variables X and Y. After that from the solution we need to find the values of X and Y for which the output will be 1.
Formula Used: In this solution we have used the following formula,
$\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$ and
$A \cdot A = A$
Complete step by step answer
Let us first redraw the diagram and give names to the various points.

Now, for the OR gate named I, the inputs are A and B. The value of A is given as, $A = \bar X$. And the value of B is Y. The output of this gate will be,
$P = A + B$,
Substituting we get,
$P = \bar X + Y$
Now gate II is an NAND gate. The inputs of this gate are named as C and D. We have the input C as X and the input D as, $D = \bar Y$
The output of an AND gate is given as, $CD$ and for a NAND gate the output will be,
$Q = \overline {C \cdot D} $
Substituting we get,
$Q = \overline {X \cdot \bar Y} $
Now the gate III is a NOR gate. The inputs of this gate are P and Q. So the output R will be,
$R = \overline {P + Q} $
Substituting the values of P and Q we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right) + \overline {X \cdot \bar Y} } $
So we can simplify this from the formula, $\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$
Therefore we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right)} \cdot \overline {\overline {X \cdot \bar Y} } $
Hence we get,
$R = \overline {\left( {\bar X + Y} \right)} \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now in the first part we can use the formula, $\overline {A + B} = \bar A \cdot \bar B$ again and get,
$R = \left( {\bar{ \bar X} \cdot \bar Y} \right) \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Hence we have,
$R = \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right) \cdot \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now since $A \cdot A = A$, so we get
$R = \left( {X \cdot \bar Y} \right)$
Now for the output R to be 1, both X and $\bar Y$ has to be 1
So the value of X is 1 and $\bar Y$ is 1. So Y is 0.
Hence X has to be 1 and Y has to be 0
Therefore the correct option is (D).
Note
A digital logic gate is an electronic circuit which makes logical decisions based on the combination of inputs. There are three basic types of logic gates, namely AND gate, OR gate and NOT gate. For the AND gate the output 1 only when both the inputs are 1. For the OR gate, the output is 1 when any one of the inputs are 1 and the NOT gate reverses the input.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




