
To form the image on the object itself, how should we place the object in front of a concave mirror? Explain with a ray diagram.
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: A concave mirror is a spherical mirror whose reflective surface is curved inwards. It is capable of producing different types of images- inverted or upright, virtual or real, enlarged or diminished. The nature of the image formed depends on the distance of the object from the pole of the mirror.
Complete answer:
A concave mirror can is a small part of a spherical-shaped mirror whose inner surface is reflective. The image formed by a concave mirror is upright and virtual when the object is situated between the focus and the pole. As the object moves towards focus it increases in size until the image size becomes infinity at the focus. After the object passes focus, it starts decreasing in size as the object continues to move backward. Finally, when the object is placed at the center of curvature the image of the object is the same size as the object. This image is inverted and real. The following ray diagram shows the nature of the image formed-
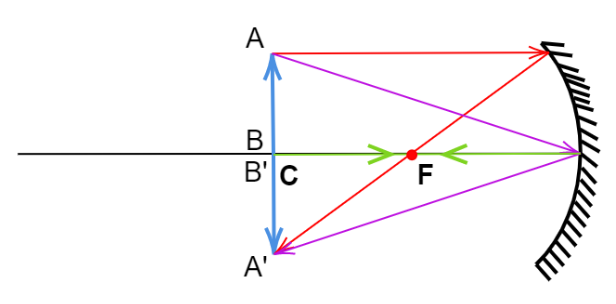
Additional Information:
While determining the nature of the image formed by a mirror, the distance of the object is measured in reference to two points-
1. The focal point- The focal point of a lens is the point where a beam of parallel rays when reflected through the mirror converges (or appears to converge ). The focal length is the distance between the pole of the mirror and the focal point. For spherical mirrors, the focal point is situated at half the distance of the center of curvature of the mirror.
2. The center of curvature- The center of curvature is the center of the original sphere that the mirror was cut out from. The distance between the pole of the mirror and the center of curvature is known as the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Note: To draw the ray diagram of a lens or a mirror, we take a minimum of three rays. If the object is placed vertically then the first ray must be parallel and originate from the top, this then passes through the focus, the other ray should be directed to the pole of the mirror, as it reflects back at the same angle. The third should originate from the bottom of the object and should be directed to the pole.
Complete answer:
A concave mirror can is a small part of a spherical-shaped mirror whose inner surface is reflective. The image formed by a concave mirror is upright and virtual when the object is situated between the focus and the pole. As the object moves towards focus it increases in size until the image size becomes infinity at the focus. After the object passes focus, it starts decreasing in size as the object continues to move backward. Finally, when the object is placed at the center of curvature the image of the object is the same size as the object. This image is inverted and real. The following ray diagram shows the nature of the image formed-

Additional Information:
While determining the nature of the image formed by a mirror, the distance of the object is measured in reference to two points-
1. The focal point- The focal point of a lens is the point where a beam of parallel rays when reflected through the mirror converges (or appears to converge ). The focal length is the distance between the pole of the mirror and the focal point. For spherical mirrors, the focal point is situated at half the distance of the center of curvature of the mirror.
2. The center of curvature- The center of curvature is the center of the original sphere that the mirror was cut out from. The distance between the pole of the mirror and the center of curvature is known as the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Note: To draw the ray diagram of a lens or a mirror, we take a minimum of three rays. If the object is placed vertically then the first ray must be parallel and originate from the top, this then passes through the focus, the other ray should be directed to the pole of the mirror, as it reflects back at the same angle. The third should originate from the bottom of the object and should be directed to the pole.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




