
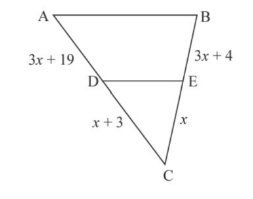
To find the value of x from the below figure such that \[DE\parallel AB\]

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: From the given figure, a line is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle. Hence, this can be solved either by applying Thales theorem or by the property of similar triangles. Line drawn parallel to one side of the triangle, intersects the other two sides in distinct points, then it divides the other two sides in the same ratio. In a similar triangle, corresponding sides are of the same ration. Hence find the corresponding sides of the same ration from the given figure. And then substituting the values on the ratio. Now cross multiplying the ratio and solving further we get the value of x.
Complete step-by-step solution:
If \[DE\parallel AB\], then \[\vartriangle CDE \sim \vartriangle ABC\], that is \[\vartriangle CDE\]is similar to \[\vartriangle ABC\]
Therefore, their corresponding sides are of same ratio
By the property of similar triangles:
Since their corresponding sides are of same ratio
\[\dfrac{{CD}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BC}}\]
Substituting the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + 3}}{{4x + 22}} = \dfrac{x}{{4x + 4}}\]
Now cross multiply,
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {x + 3} \right)\left( {4x + 4} \right) = x\left( {4x + 22} \right)\]
Further multiplication,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 4x + 12x + 12 = 4{x^2} + 22x\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 16x + 12 = 4{x^2} + 22x\]
Now keeping the higher order on one side and the remaining on the other side,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 16x + 12 - 4{x^2} - 22x = 0\]
Simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 12 - 6x = 0\]
Solve it for x, rearranging the terms
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 6x\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{12}}{6}\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
The value of x is equal to 2.
Note: Alternative method: Using basic property theorem of Thales theorem
Basic property theorem: If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. That is also known as Thales theorem.
Since \[DE\parallel AB\],
\[\dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{BE}}{{EC}}\]
Applying the values,
\[\dfrac{{3x + 19}}{{x + 3}} = \dfrac{{3x + 4}}{x}\]
Cross multiplying,
\[\left( {3x + 19} \right) \times x = \left( {3x + 4} \right) \times \left( {x + 3} \right)\]
Multiply the terms we get,
\[3{x^2} + 19x = 3{x^2} + 9x + 4x + 12\]
Simplifying we get,
\[3{x^2} + 19x = 3{x^2} + 13x + 12\]
Cancelling the similar terms,
\[19x = 13x + 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6x = 12\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Hence, the value is \[x = 2\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
If \[DE\parallel AB\], then \[\vartriangle CDE \sim \vartriangle ABC\], that is \[\vartriangle CDE\]is similar to \[\vartriangle ABC\]
Therefore, their corresponding sides are of same ratio
By the property of similar triangles:
Since their corresponding sides are of same ratio
\[\dfrac{{CD}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BC}}\]
Substituting the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + 3}}{{4x + 22}} = \dfrac{x}{{4x + 4}}\]
Now cross multiply,
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {x + 3} \right)\left( {4x + 4} \right) = x\left( {4x + 22} \right)\]
Further multiplication,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 4x + 12x + 12 = 4{x^2} + 22x\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 16x + 12 = 4{x^2} + 22x\]
Now keeping the higher order on one side and the remaining on the other side,
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 16x + 12 - 4{x^2} - 22x = 0\]
Simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 12 - 6x = 0\]
Solve it for x, rearranging the terms
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 6x\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{12}}{6}\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
The value of x is equal to 2.
Note: Alternative method: Using basic property theorem of Thales theorem
Basic property theorem: If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. That is also known as Thales theorem.
Since \[DE\parallel AB\],
\[\dfrac{{AD}}{{DC}} = \dfrac{{BE}}{{EC}}\]
Applying the values,
\[\dfrac{{3x + 19}}{{x + 3}} = \dfrac{{3x + 4}}{x}\]
Cross multiplying,
\[\left( {3x + 19} \right) \times x = \left( {3x + 4} \right) \times \left( {x + 3} \right)\]
Multiply the terms we get,
\[3{x^2} + 19x = 3{x^2} + 9x + 4x + 12\]
Simplifying we get,
\[3{x^2} + 19x = 3{x^2} + 13x + 12\]
Cancelling the similar terms,
\[19x = 13x + 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6x = 12\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Hence, the value is \[x = 2\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE

What is the full form of pH?





