
To construct a ray diagram, we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the lens. List the two rays and state the path of these rays after refraction. Use these two rays to locate the image of an object placed between and of convex lens.
Answer
549.3k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are going to first construct the ray diagram for the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and the focus of the mirror and list the two type of rays that are formed after refraction.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first construct the ray diagram for an object lying in front of the concave mirror and the corresponding image formation.
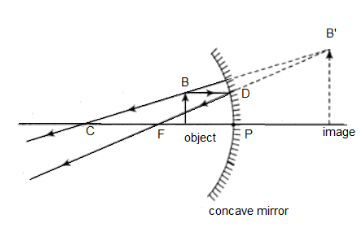
The two types of rays that we need to list here in the question are:
i) The ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis, it passes through the point $ F $ of the concave mirror after its reflection.
Ii) The ray of light passing through the point $ C $ of the mirror, is reflected back on the same path after reflection from the mirror.
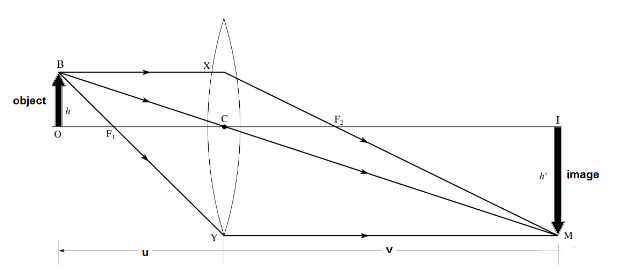
In the ray diagram below, as we can see that the object is placed in between the points and of the convex lens. In this case, the image is formed beyond the lens, is greater than the size of the image and is formed behind the $ 2F $ .
Note:
It is important to note that the convex lens and the concave mirror show a similar behavior in many cases, like those including the formation of a real or a virtual image. But specific cases of different objects placed at the different points for the convex lens and the concave mirror are completely different.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first construct the ray diagram for an object lying in front of the concave mirror and the corresponding image formation.

The two types of rays that we need to list here in the question are:
i) The ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis, it passes through the point $ F $ of the concave mirror after its reflection.
Ii) The ray of light passing through the point $ C $ of the mirror, is reflected back on the same path after reflection from the mirror.
In the ray diagram below, as we can see that the object is placed in between the points and of the convex lens. In this case, the image is formed beyond the lens, is greater than the size of the image and is formed behind the $ 2F $ .

Note:
It is important to note that the convex lens and the concave mirror show a similar behavior in many cases, like those including the formation of a real or a virtual image. But specific cases of different objects placed at the different points for the convex lens and the concave mirror are completely different.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




