
Through the midpoint M of the side CD of a parallelogram ABCD, the line BM is drawn intersecting AC at L and AD produced at E. Prove that $ EL = 2BL $ .
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To derive required proof, we first prove triangles BMC and triangle DME are congruent and then prove triangle ALE and triangle BLC similar and substituting values in ratio of sides obtained from similar triangles to get required proof.
Complete step-by-step answer:
ABCD is a parallelogram. M is the midpoint of CD.
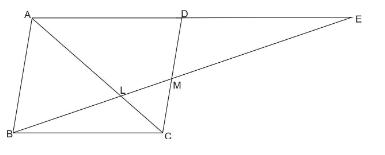
In $ \Delta BCM\,\,and\,\Delta EDM $
CM = DM (M is midpoint of CD)
$
\angle BMC = \angle DME\,\,\left( {Vertical\,\,opposite} \right) \\
\angle BCM = \angle EDM\,\,\left( {alternate\,\,\operatorname{int} erior\,\,angles} \right) \\
\therefore \Delta BCM \cong \Delta EDM\,\,\left( {ASA\,\,\,congurence} \right) \\
$
$ \Rightarrow BC = DE\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( {by\,\,CPCT} \right) $
Also, BC = AD (opposite side of a ||gm ABCD)
Adding above two equations we have,
$
BC + BC = AD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 2BC = AE..............(i) \\
$
Now, in $ \Delta $ BLC and $ \Delta $ ALE, we have
\[
\angle EAL = \angle BCL (\because \text{alternate angles}) \\
\angle BCL = \angle AEL (\because \text{alternate angles})\;
\]
$ \therefore \Delta BCL \sim \Delta ELA $
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AE}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{2BC}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow EL = 2BL \;
$
Which is the required proof.
Note: In geometric proof, to derive required proof we must go through the statement carefully and then use different conditions given in the problem as in either similarities or congruence of triangle to prove required proof asked in question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
ABCD is a parallelogram. M is the midpoint of CD.

In $ \Delta BCM\,\,and\,\Delta EDM $
CM = DM (M is midpoint of CD)
$
\angle BMC = \angle DME\,\,\left( {Vertical\,\,opposite} \right) \\
\angle BCM = \angle EDM\,\,\left( {alternate\,\,\operatorname{int} erior\,\,angles} \right) \\
\therefore \Delta BCM \cong \Delta EDM\,\,\left( {ASA\,\,\,congurence} \right) \\
$
$ \Rightarrow BC = DE\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( {by\,\,CPCT} \right) $
Also, BC = AD (opposite side of a ||gm ABCD)
Adding above two equations we have,
$
BC + BC = AD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 2BC = AE..............(i) \\
$
Now, in $ \Delta $ BLC and $ \Delta $ ALE, we have
\[
\angle EAL = \angle BCL (\because \text{alternate angles}) \\
\angle BCL = \angle AEL (\because \text{alternate angles})\;
\]
$ \therefore \Delta BCL \sim \Delta ELA $
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AE}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{2BC}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BL}}{{EL}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow EL = 2BL \;
$
Which is the required proof.
Note: In geometric proof, to derive required proof we must go through the statement carefully and then use different conditions given in the problem as in either similarities or congruence of triangle to prove required proof asked in question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




