
Three waves of equal frequency having amplitudes 10mm, 4mm and 7mm arrive at a given point with successive phase difference $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . The amplitude of the resulting wave (in mm) given by:
A. 7
B. 6
C. 5
D. 4
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Amplitudes of sinusoidally varying quantities behave as vectors and the phase difference act as angles between the vectors. So, we can add them in that method to find the amplitude of the resultant wave.
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, it is given that the three waves arrive at point with successive difference of ${{90}^{\circ }}$
So, consider that the amplitude of the first wave is along the x-axis, the second wave along y-axis and the third wave along the negative x-axis.
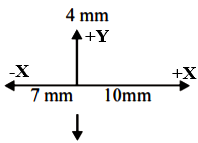
The waves of amplitude 10mm and 7mm will completely be out of phase and destructively interfere.
The amplitude of the resultant wave will be $10-7=3mm$
Let us now consider that the waves of amplitude 3mm and 4mm are out of phase by ${{90}^{\circ }}$
We shall apply the Pythagoras theorem to find the new amplitude of wave that will emerge when these two interfere with each other
${{A}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}$
${{A}^{2}}=25$
$A=5mm$
Therefore, the correct answer for the given question is option (C).
Note: There is another method to solve this question,
Consider the wave equations as
$\begin{align}
& {{X}_{1}}=10\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
& {{X}_{2}}=4\sin \left( \omega t+\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \\
& {{X}_{3}}=7\sin \left( \omega t+\pi \right) \\
\end{align}$
On solving the phase difference, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{X}_{2}}=4\cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
& {{X}_{3}}=-7\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
\end{align}$
The disturbance according to the superposition theorem is calculated as
$\begin{align}
& X={{X}_{1}}+{{X}_{2}}+{{X}_{3}} \\
& X=10\sin \left( \omega t \right)+4\cos \left( \omega t \right)-7\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
& X=3\sin \left( \omega t \right)+4\cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let’s assume ‘R’ to be the resultant amplitude
$\begin{align}
& 3=R\cos \phi \\
& 4=R\sin \phi \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the equation becomes
$\begin{align}
& X=R\cos \phi \sin \left( \omega t \right)+R\sin \phi \cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
& X=R\sin \left( \omega t+\phi \right) \\
\end{align}$
$R=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}}=5mm$
The answer for the given question is option (C).
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, it is given that the three waves arrive at point with successive difference of ${{90}^{\circ }}$
So, consider that the amplitude of the first wave is along the x-axis, the second wave along y-axis and the third wave along the negative x-axis.

The waves of amplitude 10mm and 7mm will completely be out of phase and destructively interfere.
The amplitude of the resultant wave will be $10-7=3mm$
Let us now consider that the waves of amplitude 3mm and 4mm are out of phase by ${{90}^{\circ }}$
We shall apply the Pythagoras theorem to find the new amplitude of wave that will emerge when these two interfere with each other
${{A}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}$
${{A}^{2}}=25$
$A=5mm$
Therefore, the correct answer for the given question is option (C).
Note: There is another method to solve this question,
Consider the wave equations as
$\begin{align}
& {{X}_{1}}=10\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
& {{X}_{2}}=4\sin \left( \omega t+\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \\
& {{X}_{3}}=7\sin \left( \omega t+\pi \right) \\
\end{align}$
On solving the phase difference, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{X}_{2}}=4\cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
& {{X}_{3}}=-7\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
\end{align}$
The disturbance according to the superposition theorem is calculated as
$\begin{align}
& X={{X}_{1}}+{{X}_{2}}+{{X}_{3}} \\
& X=10\sin \left( \omega t \right)+4\cos \left( \omega t \right)-7\sin \left( \omega t \right) \\
& X=3\sin \left( \omega t \right)+4\cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let’s assume ‘R’ to be the resultant amplitude
$\begin{align}
& 3=R\cos \phi \\
& 4=R\sin \phi \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the equation becomes
$\begin{align}
& X=R\cos \phi \sin \left( \omega t \right)+R\sin \phi \cos \left( \omega t \right) \\
& X=R\sin \left( \omega t+\phi \right) \\
\end{align}$
$R=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}}=5mm$
The answer for the given question is option (C).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




