
Three rods of copper, Brass, Steel are welded together to form a Y-shaped structure. Area of cross section. Area of cross section of each rod $ = 4c{m^2} $ . End of copper rod is maintained at $ {100^ \circ }C $ whereas ends of brass and steel are kept at $ {0^ \circ }C $ . Lengths of the copper, brass and steel rods are $ 46,13\,\,and\,12cms $ respectively. The rods are thermally insulated from surroundings except at ends. Thermal conductivities of copper, brass and steel are $ 0.92 $ , $ 0.26 $ and $ 0.12 $ CGS units respectively. Rate of heat flow through copper rod is:
$ \left( A \right)4.8cal{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( B \right)6cal{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( C \right)1.2cal{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( D \right)2.4cal{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to first write the relation for the heat change per unit time and then, using the principles of the thermal conductivity, we get the value for the rate of heat flow through the copper rod using the relations and putting value of the common temperature in them.
In thermal conduction, the equation can be written as
$ \dfrac{{\Delta Q}}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{kA\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right)}}{x} $
The heat exchange system that can be seen above gives the relation
$ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{d{Q_2}}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d{Q_3}}}{{dt}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In thermal conduction, it is found that in the steady state, the heat current is directly proportional to the area of the cross section $ A $ which is further directly proportional to the change in the temperature, $ {T_2} - {T_1} $ .
Thus, we can write the equation as:
$ \dfrac{{\Delta Q}}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{kA\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right)}}{x} $
According to the thermal conductivity, we get
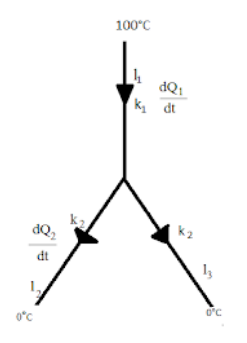
The heat exchange system that can be seen above gives the relation
$ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{d{Q_2}}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d{Q_3}}}{{dt}} $
Putting the values from the above equation, we get
$ \dfrac{{0.92\left( {100 - T} \right)}}{{46}} = \dfrac{{0.26\left( {T - 0} \right)}}{{13}} + \dfrac{{0.12\left( {T - 0} \right)}}{{12}} $
As the temperature $ {40^ \circ }C $ , if we calculate the rate of change of heat, $ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} $ , then,
$ \dfrac{{0.92 \times 4\left( {100 - 40} \right)}}{{46}} = 4.8cal{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Note :
If the length of the rod and the temperature changes corresponding to the different types of the materials is the same, then the only factor on which the rate of change of the heat depends is the thermal conductivity. This gives the net change for the heat current in the bodies.
In thermal conduction, the equation can be written as
$ \dfrac{{\Delta Q}}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{kA\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right)}}{x} $
The heat exchange system that can be seen above gives the relation
$ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{d{Q_2}}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d{Q_3}}}{{dt}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In thermal conduction, it is found that in the steady state, the heat current is directly proportional to the area of the cross section $ A $ which is further directly proportional to the change in the temperature, $ {T_2} - {T_1} $ .
Thus, we can write the equation as:
$ \dfrac{{\Delta Q}}{{\Delta t}} = \dfrac{{kA\left( {{T_1} - {T_2}} \right)}}{x} $
According to the thermal conductivity, we get

The heat exchange system that can be seen above gives the relation
$ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{d{Q_2}}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d{Q_3}}}{{dt}} $
Putting the values from the above equation, we get
$ \dfrac{{0.92\left( {100 - T} \right)}}{{46}} = \dfrac{{0.26\left( {T - 0} \right)}}{{13}} + \dfrac{{0.12\left( {T - 0} \right)}}{{12}} $
As the temperature $ {40^ \circ }C $ , if we calculate the rate of change of heat, $ \dfrac{{d{Q_1}}}{{dt}} $ , then,
$ \dfrac{{0.92 \times 4\left( {100 - 40} \right)}}{{46}} = 4.8cal{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Note :
If the length of the rod and the temperature changes corresponding to the different types of the materials is the same, then the only factor on which the rate of change of the heat depends is the thermal conductivity. This gives the net change for the heat current in the bodies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




