
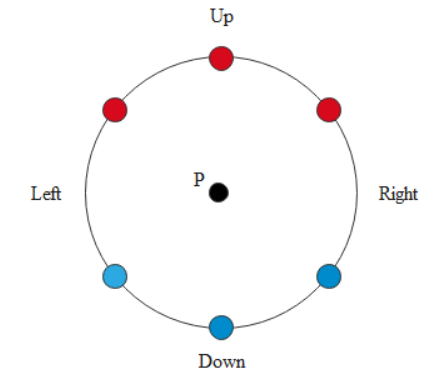
Three positive (red) and three negative (blue) point charges are arranged symmetrically around a circle centered on point P as shown in the diagram below.
All point charges are of the same magnitude.
Which option gives the best description of the electric field at point P and the electric potential at point P?
A. Electric field at P – Electrical potential at P, Zero – Zero
B. Electric field at P – Electrical potential at P, downward – downward
C. Electric field at P – Electrical potential at P, upward – positive
D. Electric field at P – Electrical potential at P, downward – zero
E. Electric field at P – Electrical potential at P, upward – zero

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The student should remember that the direction of the electric field is always directed from the positive charge to the negative charge. We know the expressions for calculating the electric field and the electric potential which will give us the required answer.
Formula used:
Electric field at a point due to a given charge q can be calculated by the following formula:
\[E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}}\]
Also we can calculate the electric potential due to the given charge q by the following formula:
$V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{q}{r}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
Here r signifies the distance of charge from the point of observation and value of $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}{C^{ - 2}}$
Detailed step by step solution:
We are given six charges as shown in the figure. We know that the direction of the electric field is always from the positive charge to the negative charge.
First, let us calculate the electric field at point P. The field due to positive charge is directed downwards and using equation (i), it can be given as
${E_1} = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
The electric field due to the negative charges is also directed downwards can be given as
${E_2} = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
Therefore, the net electric field at P is equal to the sum of fields due to positive and negative charge and can be given as
$E = {E_1} + {E_2} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{6kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
Now the electric potential at P can be calculated using equation (ii) as follows:
$V = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = 0$
Therefore, based on our calculations, we can say that the correct answer is option D.
Note: The electric field is a vector quantity while the electric potential is a scalar quantity. We have obtained results for electric fields using vector addition while the electric potential is obtained using simple addition based on sign of the charges.
Formula used:
Electric field at a point due to a given charge q can be calculated by the following formula:
\[E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}}\]
Also we can calculate the electric potential due to the given charge q by the following formula:
$V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{q}{r}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}}$
Here r signifies the distance of charge from the point of observation and value of $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}{C^{ - 2}}$
Detailed step by step solution:
We are given six charges as shown in the figure. We know that the direction of the electric field is always from the positive charge to the negative charge.
First, let us calculate the electric field at point P. The field due to positive charge is directed downwards and using equation (i), it can be given as
${E_1} = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
The electric field due to the negative charges is also directed downwards can be given as
${E_2} = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
Therefore, the net electric field at P is equal to the sum of fields due to positive and negative charge and can be given as
$E = {E_1} + {E_2} = \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{3kq}}{{{r^2}}} = \dfrac{{6kq}}{{{r^2}}}$ (downwards)
Now the electric potential at P can be calculated using equation (ii) as follows:
$V = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} - \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}} = 0$
Therefore, based on our calculations, we can say that the correct answer is option D.
Note: The electric field is a vector quantity while the electric potential is a scalar quantity. We have obtained results for electric fields using vector addition while the electric potential is obtained using simple addition based on sign of the charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




