
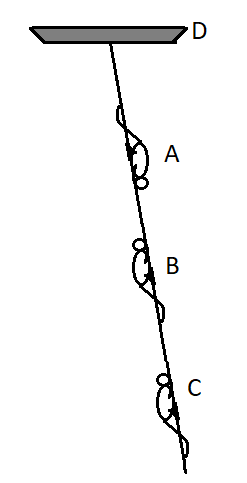
Three monkeys A, B, C with masses of 10, 15, 8 kg respectively are climbing up and down the rope suspended from D. At the instant represented, A is descending the rope with an acceleration of $ 2m/{s^2} $ and C is pulling himself up with an acceleration of $ 1.5m/{s^2} $ . Monkey B is climbing up with a constant speed of $ 0.8m/s $ . Treat the rope and monkeys as a complete system and calculate the tension T in the rope at D. $ \left( {g = 10m/{s^2}} \right) $

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint We need to draw the free body diagrams of each of the monkeys. We consider the tensions for each part of the wire different. Then from the equations of motions of each of the monkeys we need to find the tension at each part. Hence we get the tension at D.
Formula Used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = ma $
where $ {F_{net}} $ is the net force on the body, $ m $ is the mass and $ a $ is the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the monkey C. The forces acting on it are the tension due to the string upwards and the mass of the monkey acting downwards. The monkey C is moving up with an acceleration of $ 1.5m/{s^2} $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey C will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} - {m_C}g = {m_C}{a_C} $
The mass of the third monkey is $ {m_C} = 8kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $\Rightarrow {a_C} = 1.5m/{s^2} $
Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} - 8 \times 10 = 8 \times 1.5 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} = \left( {8 \times 1.5} \right) + \left( {8 \times 10} \right) $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} = 92N $
Now for the second monkey B, the forces acting on it are the tension due to the string $ {T_2} $ upwards and the mass of the monkey and the tension $ {T_3} = 92N $ acting downwards. The monkey B is moving up with a constant speed of $ 0.8m/s $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey B will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} - {T_3} - {m_B}g = {m_B}{a_B} $
The mass of the second monkey is $ {m_B} = 15kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $ {a_B} = 0 $ since speed is constant. Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} - 92 - \left( {15 \times 10} \right) = 0 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} = 92 + 150 $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} = 242N $
Now for the first monkey A, the forces acting on it are the tension due to the string $ {T_1} $ upwards and the mass of the monkey and the tension $ {T_2} = 242N $ acting downwards. The monkey A is moving down with a constant acceleration of $ 2m/{s^2} $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey A will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} + {m_A}g - {T_1} = {m_A}{a_A} $
The mass of the first monkey is $ {m_A} = 10kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $ {a_A} = 2m/{s^2} $ Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow 242 + \left( {10 \times 10} \right) - {T_1} = 10 \times 2 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_1} = 242 + 100 - 20 $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_1} = 322N $
So the tension on the rope at the point D will be $ {T_1} = 322N $ .
Note
Here we have used the free body diagrams of each of the monkeys to calculate the tension in the string. The free body diagram is a graphical illustration which is used to represent the forces acting on the body and the direction of motion of the body due to the net for acting on it.
Formula Used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = ma $
where $ {F_{net}} $ is the net force on the body, $ m $ is the mass and $ a $ is the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the monkey C. The forces acting on it are the tension due to the string upwards and the mass of the monkey acting downwards. The monkey C is moving up with an acceleration of $ 1.5m/{s^2} $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey C will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} - {m_C}g = {m_C}{a_C} $
The mass of the third monkey is $ {m_C} = 8kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $\Rightarrow {a_C} = 1.5m/{s^2} $
Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} - 8 \times 10 = 8 \times 1.5 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} = \left( {8 \times 1.5} \right) + \left( {8 \times 10} \right) $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_3} = 92N $
Now for the second monkey B, the forces acting on it are the tension due to the string $ {T_2} $ upwards and the mass of the monkey and the tension $ {T_3} = 92N $ acting downwards. The monkey B is moving up with a constant speed of $ 0.8m/s $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey B will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} - {T_3} - {m_B}g = {m_B}{a_B} $
The mass of the second monkey is $ {m_B} = 15kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $ {a_B} = 0 $ since speed is constant. Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} - 92 - \left( {15 \times 10} \right) = 0 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} = 92 + 150 $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} = 242N $
Now for the first monkey A, the forces acting on it are the tension due to the string $ {T_1} $ upwards and the mass of the monkey and the tension $ {T_2} = 242N $ acting downwards. The monkey A is moving down with a constant acceleration of $ 2m/{s^2} $ .
So the equation of motion of the monkey A will be,
$\Rightarrow {T_2} + {m_A}g - {T_1} = {m_A}{a_A} $
The mass of the first monkey is $ {m_A} = 10kg $ , $ g = 10m/{s^2} $ and the acceleration is $ {a_A} = 2m/{s^2} $ Therefore on substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow 242 + \left( {10 \times 10} \right) - {T_1} = 10 \times 2 $
So we get the tension as,
$\Rightarrow {T_1} = 242 + 100 - 20 $
Hence on calculating e get,
$\Rightarrow {T_1} = 322N $
So the tension on the rope at the point D will be $ {T_1} = 322N $ .
Note
Here we have used the free body diagrams of each of the monkeys to calculate the tension in the string. The free body diagram is a graphical illustration which is used to represent the forces acting on the body and the direction of motion of the body due to the net for acting on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




