
Three long, straight and parallel wires are arranged as shown in figure. The force
experienced by 10 cm length of wire $Q$ is
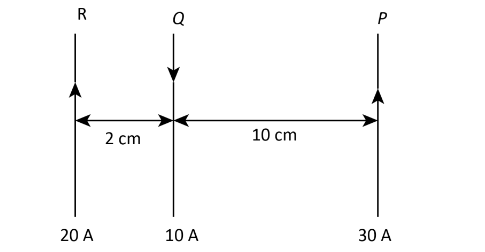
A. $1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ toward the right
B. $1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ towards the left
C. $2.6 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ toward the right
D. $2.6 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ toward the left

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Find the magnetic field due to $R$ on Q and due to $P$on $Q$ and use this expression to find the force and when the current are in opposite direction in the straight conductor, then the force is repulsive in nature.
Formula used: The magnetic field due to infinitely long straight conductor: $B = \dfrac{{{\mu
_0}I}}{{2\pi a}}$
Complete step by step answer:
From the given question, we know that the current in wire $P.\;Q$ and $R$ are ${I_P} =
30\;{\rm{A}}$, ${I_Q} = 10{\rm{A}}$ and ${I_R} = 20\;{\rm{A}}$, the distance between the wire
$R\;$ and $Q$ is ${a_{RQ}} = 0.02\;{\rm{m}}$, the distance between the wire $P$ and $Q$ is
${a_{PQ}} = 0.1\;{\rm{m}}$ and the length of the wire $Q$ is $L = 0.1\;{\rm{m}}$
The magnetic field produced by wire $R$ at $Q$ is expressed as,
${B_{RQ}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}}$
Since the force experienced by wire $Q$ is in left direction (repulsion) as the directions of the
current are anti parallel and it is calculated as,
$
{F_{RQ}} = {I_Q}L{B_{RQ}}\\
{F_{RQ}} = {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}}
$
Similarly, the magnetic field produced by wire $P$ at $Q$ is expressed as,
${B_{PQ}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}$
Since the force experienced by wire $Q$ is in right direction (repulsion) as the directions of the
current are anti parallel and it is calculated as,
$
{F_{PQ}} = {I_Q}L{B_{PQ}}\\
{F_{PQ}} = {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}
$
The net force experienced by the wire $Q$ is calculated as,
$
F = {F_{RQ}} - {F_{PQ}}\\
= {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}} - {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}\\
= \dfrac{{{I_Q}L{\mu _0}}}{{2\pi }}\left[ {\dfrac{{{I_R}}}{{{a_{RQ}}}} - \dfrac{{{I_P}}}{{{a_{PQ}}}}}
\right]\\
= \dfrac{{10 \times 0.1 \times 4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}}}}{{2\pi }}\left[ {\dfrac{{20}}{{0.02}} -
\dfrac{{30}}{{0.1}}} \right]\\
= 1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}\;\;{\rm{towards}}\;{\rm{right}}
$
Thus, the force experienced by the wire $Q$ is $1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ toward right
direction and option (A) is correct.
Note: Be careful while answering, because the formula for finite straight wire and infinite
straight are completely different.
When wire has finite length: \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}\left( {\sin {\phi _2} + \sin {\phi
_1}} \right)\]
When wire has infinite length, ${\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 90^\circ $: \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi
a}}\]
When wire has infinite length and point $P$ lies at near wire’s end, ${\phi _1} = 90^\circ
\;{\rm{and}}\;{\phi _2} = 0$:
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}\]
Formula used: The magnetic field due to infinitely long straight conductor: $B = \dfrac{{{\mu
_0}I}}{{2\pi a}}$
Complete step by step answer:
From the given question, we know that the current in wire $P.\;Q$ and $R$ are ${I_P} =
30\;{\rm{A}}$, ${I_Q} = 10{\rm{A}}$ and ${I_R} = 20\;{\rm{A}}$, the distance between the wire
$R\;$ and $Q$ is ${a_{RQ}} = 0.02\;{\rm{m}}$, the distance between the wire $P$ and $Q$ is
${a_{PQ}} = 0.1\;{\rm{m}}$ and the length of the wire $Q$ is $L = 0.1\;{\rm{m}}$
The magnetic field produced by wire $R$ at $Q$ is expressed as,
${B_{RQ}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}}$
Since the force experienced by wire $Q$ is in left direction (repulsion) as the directions of the
current are anti parallel and it is calculated as,
$
{F_{RQ}} = {I_Q}L{B_{RQ}}\\
{F_{RQ}} = {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}}
$
Similarly, the magnetic field produced by wire $P$ at $Q$ is expressed as,
${B_{PQ}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}$
Since the force experienced by wire $Q$ is in right direction (repulsion) as the directions of the
current are anti parallel and it is calculated as,
$
{F_{PQ}} = {I_Q}L{B_{PQ}}\\
{F_{PQ}} = {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}
$
The net force experienced by the wire $Q$ is calculated as,
$
F = {F_{RQ}} - {F_{PQ}}\\
= {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_R}}}{{2\pi {a_{RQ}}}} - {I_Q}L\dfrac{{{\mu _0}{I_P}}}{{2\pi {a_{PQ}}}}\\
= \dfrac{{{I_Q}L{\mu _0}}}{{2\pi }}\left[ {\dfrac{{{I_R}}}{{{a_{RQ}}}} - \dfrac{{{I_P}}}{{{a_{PQ}}}}}
\right]\\
= \dfrac{{10 \times 0.1 \times 4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}}}}{{2\pi }}\left[ {\dfrac{{20}}{{0.02}} -
\dfrac{{30}}{{0.1}}} \right]\\
= 1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}\;\;{\rm{towards}}\;{\rm{right}}
$
Thus, the force experienced by the wire $Q$ is $1.4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\rm{N}}$ toward right
direction and option (A) is correct.
Note: Be careful while answering, because the formula for finite straight wire and infinite
straight are completely different.
When wire has finite length: \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}\left( {\sin {\phi _2} + \sin {\phi
_1}} \right)\]
When wire has infinite length, ${\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 90^\circ $: \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi
a}}\]
When wire has infinite length and point $P$ lies at near wire’s end, ${\phi _1} = 90^\circ
\;{\rm{and}}\;{\phi _2} = 0$:
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




