
Three floral diagrams are given here. Their respective families are assigned in the answer key. Find out the families to which these diagrams belong to.
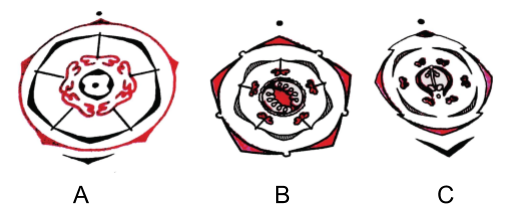
(a) A - Liliaceae, B - Asteraceae, C - Solanaceae
(b) A - Asteraceae, B - Solanaceae, C - Brassicaceae
(c) A - Asteraceae, B - Solanaceae, C - Asteraceae
(d) A - Poaceae, B - Solanaceae, C - Asteraceae

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The first floral diagram belongs to the family that includes floral plants like garden marigold. Atropa belladonna is an example of the second family, while the third floral diagram represents the family which is commonly called the cabbage family.
Complete answer:
The diagram ‘A’ belongs to the family Asteraceae, ‘B’ belongs to Solanaceae and ‘C’ represents Brassicaceae.
Let's first learn about family Asteraceae.
-In the family Asteraceae, both the five sepals and five petals are arranged in valvate aestivation.
-There are a total of 5 stamens arranged in an epipetalous condition. This means that the stamens are fused with petals.
-The ovary in the family Asteraceae exhibits basal placentation.
Now let's study about family Solanaceae.
-The family Solanaceae exhibits 5 sepals that are united, persistent, and show valvate aestivation.
-The arrangement of petals is as follows: There are five petals, united and show valvate aestivation.
-There is a presence of 5 stamens in an epipetalous fashion i.e. stamens are fused with petals.
-The gynoecium is bicarpellary, obligately placed. The ovary is syncarpous, superior, and bilocular.
-The placenta is swollen with many ovules and shows axile placentation.
The features of the family Brassicaceae in brief are:
-The family Brassicaceae exhibits 4 sepals in two whorls with imbricate aestivation.
-The arrangement of petals is valvate aestivation.
-There are a total of six stamens arranged in two worlds in a tetradynamous condition. It is a condition where among the five stamens four stamens are long while two are short.
-The gynoecium is bicarpellary with the false separation between two locules.
So, the correct answer is, ‘A - Asteraceae, B - Solanaceae, C - Brassicaceae.’
Note: -The family Liliaceae exhibits 6 tepals often united into a tube showing valvate aestivation. There are a total of six stamens arranged in an epipetalous fashion. Here the gynoecium has tricarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation.
-In the family Poaceae that are usually three stamens. The gynoecium is monocarpellary with superior, unilocular ovule and axile placentation.
Complete answer:
The diagram ‘A’ belongs to the family Asteraceae, ‘B’ belongs to Solanaceae and ‘C’ represents Brassicaceae.
Let's first learn about family Asteraceae.
-In the family Asteraceae, both the five sepals and five petals are arranged in valvate aestivation.
-There are a total of 5 stamens arranged in an epipetalous condition. This means that the stamens are fused with petals.
-The ovary in the family Asteraceae exhibits basal placentation.
Now let's study about family Solanaceae.
-The family Solanaceae exhibits 5 sepals that are united, persistent, and show valvate aestivation.
-The arrangement of petals is as follows: There are five petals, united and show valvate aestivation.
-There is a presence of 5 stamens in an epipetalous fashion i.e. stamens are fused with petals.
-The gynoecium is bicarpellary, obligately placed. The ovary is syncarpous, superior, and bilocular.
-The placenta is swollen with many ovules and shows axile placentation.
The features of the family Brassicaceae in brief are:
-The family Brassicaceae exhibits 4 sepals in two whorls with imbricate aestivation.
-The arrangement of petals is valvate aestivation.
-There are a total of six stamens arranged in two worlds in a tetradynamous condition. It is a condition where among the five stamens four stamens are long while two are short.
-The gynoecium is bicarpellary with the false separation between two locules.
So, the correct answer is, ‘A - Asteraceae, B - Solanaceae, C - Brassicaceae.’
Note: -The family Liliaceae exhibits 6 tepals often united into a tube showing valvate aestivation. There are a total of six stamens arranged in an epipetalous fashion. Here the gynoecium has tricarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation.
-In the family Poaceae that are usually three stamens. The gynoecium is monocarpellary with superior, unilocular ovule and axile placentation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




