
Three blocks of A, B and C, of masses $4Kg$, $2Kg$ and $1Kg$ respectively, are in contact on a frictionless surface, as shown. If a force of $14N$ is applied on the $4Kg$ block, then the contact force between A and B is:
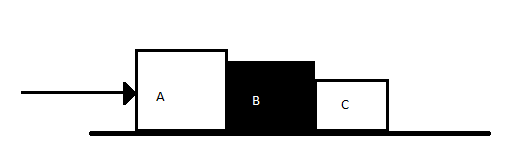
$A.8N$
$B.18N$
$C.2N$
$D.6N$

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we have to apply the concept of force and acceleration. We have to use Newton’s second law of motion. We should make a free body diagram for the blocks given above. Frictionless surface means that there is no resistance between a surface and the blocks. Contact force always occurs when the surfaces are in contact.
Formula used:
To solve this problem we have to use the following relation:-
$F=ma$.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the following figure:-
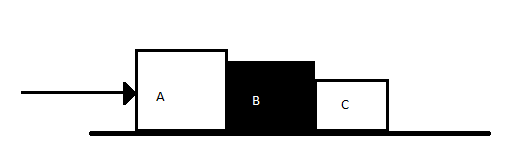
From the question we have the following parameters with us:-
Mass of A, ${{m}_{A}}=4Kg$
Mass of B, ${{m}_{B}}=2Kg$
Mass of C, ${{m}_{C}}=1Kg$
Force applied on A, ${{F}_{A}}=14N$
We know that $F=ma$…………….. $(i)$
From $(i)$we get,
$a=\dfrac{F}{m}$
Now, for all the blocks there is a common acceleration, ${{a}_{c}}$ which is given as follows:-
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{F}_{A}}}{{{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}+{{m}_{C}}}$
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{14}{4+2+1}$
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{14}{7}$
${{a}_{c}}=2m/{{s}^{2}}$
Therefore, we get the common acceleration for all the given blocks.
Now, to get the contact force between A and B we have to draw the free body diagram for block A. following is the free body diagram of block A:-
Where, $F1$ denotes force between A and B, $W$ is the weight of A and $NR$ represents normal reaction. Weight and the normal reaction cancel out each other.
From this free body diagram we get,
Net force, ${{F}_{AB}}$ between A and B as follows:-
${{F}_{AB}}={{F}_{A}}-F1$………………. $(ii)$
But, ${{F}_{AB}}=4\times 2$
${{F}_{AB}}=8N$…………….. $(iii)$
Putting the values in $(ii)$we get,
$8=14-F1$(As ${{F}_{A}}=14N$)
$F1=14-8$
$F1=6N$
∴ Option $(D)$ is correct.
Note: In solving these problems from kinematics we have to take care about the diagram and direction of the given forces. Drawing a correct free body diagram is also a very important part of the solution. Consideration of a smooth surface is also very important. Concept of common acceleration is also a very important point to ponder.
Formula used:
To solve this problem we have to use the following relation:-
$F=ma$.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the following figure:-

From the question we have the following parameters with us:-
Mass of A, ${{m}_{A}}=4Kg$
Mass of B, ${{m}_{B}}=2Kg$
Mass of C, ${{m}_{C}}=1Kg$
Force applied on A, ${{F}_{A}}=14N$
We know that $F=ma$…………….. $(i)$
From $(i)$we get,
$a=\dfrac{F}{m}$
Now, for all the blocks there is a common acceleration, ${{a}_{c}}$ which is given as follows:-
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{F}_{A}}}{{{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}}+{{m}_{C}}}$
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{14}{4+2+1}$
${{a}_{c}}=\dfrac{14}{7}$
${{a}_{c}}=2m/{{s}^{2}}$
Therefore, we get the common acceleration for all the given blocks.
Now, to get the contact force between A and B we have to draw the free body diagram for block A. following is the free body diagram of block A:-
Where, $F1$ denotes force between A and B, $W$ is the weight of A and $NR$ represents normal reaction. Weight and the normal reaction cancel out each other.
From this free body diagram we get,
Net force, ${{F}_{AB}}$ between A and B as follows:-
${{F}_{AB}}={{F}_{A}}-F1$………………. $(ii)$
But, ${{F}_{AB}}=4\times 2$
${{F}_{AB}}=8N$…………….. $(iii)$
Putting the values in $(ii)$we get,
$8=14-F1$(As ${{F}_{A}}=14N$)
$F1=14-8$
$F1=6N$
∴ Option $(D)$ is correct.
Note: In solving these problems from kinematics we have to take care about the diagram and direction of the given forces. Drawing a correct free body diagram is also a very important part of the solution. Consideration of a smooth surface is also very important. Concept of common acceleration is also a very important point to ponder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




