
This on reductive ozonolysis yields:
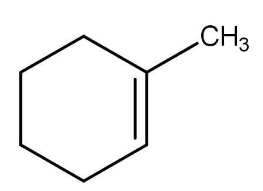
A. 6-oxoheptanal
B. 6-oxoheptanoic acid
C. 6-hydroxyheptanal
D. 3-hydroxypentanal

Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: The product formed is an aldehyde. An aldehyde is a functional group which is written as \[{\text{ }} - {\text{CHO}}\,\]. Oxo is used when oxygen is used as a functional group. Hept is used to indicate that the number of carbon in a chain is seven.
Complete step-by-step answer:
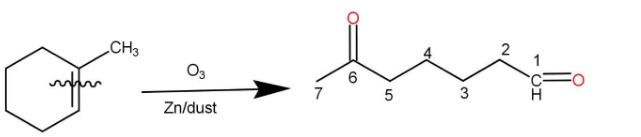
The given compound is methyl cyclohexene and ozone is trioxygen that is \[{\text{ }}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{ }}\] . Methyl cyclohexene reacts with ozone in the presence of zinc dust and produces a linear chain aldehyde, that is 6-oxoheptanal, the reaction occurs as follow:
In reductive ozonolysis, the unsaturated bonds of alkenes and alkynes are cleaved in the presence of oxygen. In unsaturated bonds double bond or triple bond is present. Alkenes are those molecules which contain double bond and alkynes are those molecules which contains triple bonds. Alkenes oxidize to form alcohol, aldehyde. ketone or carboxylic acid on reaction with ozone.
The carbon, carbon double bond upon ozonolyses breaks up and on the each carbon associated with double bond and carbon, oxygen double bond forms.
Ozonide as an intermediate is formed during the ozonolysis. Certain Reagents are used to convert intermediate ozonides formed to a carbonyl derivative. The use of zinc dust, thiourea dimethyl sulfide produces aldehyde or ketone and if we use sodium borohydride it produces alcohol and carboxylic acids are produced using hydrogen peroxide as a reagent.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Reducing agents to convert ozonide are preferred more than oxidizing agents. Zinc dust, thiourea, sodium borohydride etc all are reducing agents that is why we name the ozonolysis as reductive ozonolysis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given compound is methyl cyclohexene and ozone is trioxygen that is \[{\text{ }}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{ }}\] . Methyl cyclohexene reacts with ozone in the presence of zinc dust and produces a linear chain aldehyde, that is 6-oxoheptanal, the reaction occurs as follow:

In reductive ozonolysis, the unsaturated bonds of alkenes and alkynes are cleaved in the presence of oxygen. In unsaturated bonds double bond or triple bond is present. Alkenes are those molecules which contain double bond and alkynes are those molecules which contains triple bonds. Alkenes oxidize to form alcohol, aldehyde. ketone or carboxylic acid on reaction with ozone.
The carbon, carbon double bond upon ozonolyses breaks up and on the each carbon associated with double bond and carbon, oxygen double bond forms.
Ozonide as an intermediate is formed during the ozonolysis. Certain Reagents are used to convert intermediate ozonides formed to a carbonyl derivative. The use of zinc dust, thiourea dimethyl sulfide produces aldehyde or ketone and if we use sodium borohydride it produces alcohol and carboxylic acids are produced using hydrogen peroxide as a reagent.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Reducing agents to convert ozonide are preferred more than oxidizing agents. Zinc dust, thiourea, sodium borohydride etc all are reducing agents that is why we name the ozonolysis as reductive ozonolysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




