
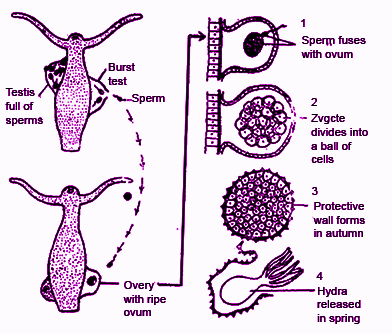
This is the figure of hydra showing its reproductive structure and manner of fertilization. Observe and answer why they cannot undergo self-fertilization?
A. Distance between testis and ovary is more
B. Sperms do not swim downwards
C. Ovary matures earlier
D. Organisms exhibit protandry. So testis have released sperms and ovary is yet to mature

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Hydra is a small, multicellular freshwater eukaryotic organism that usually reproduces asexually by budding (a process by which a small part of the adult structure becomes new). But sexual reproduction occurs in some Hydra. Swelling in the body wall develops either into ovaries or testis. Cross-fertilization occurs in Hydra.
Complete answer: Cross fertilization occurs in Hydra. In Hydra, the testis matures earlier than the ovary. Testis releases mature sperm cells that swim in the water with the help of tail and through water, it reaches to the second Hydra. One of the sperm comes into contact with the ovum and fertilised female egg develops into a zygote. The body of the Hydra looks like a tube with tentacles arranged around the head pole of the organism. The reproductive structures of hydra consist of the testis (produce sperm cells) and the ovary (produces the egg) that are located under the ectoderm. The testis is formed near the oral end of the hydra while the ovaries formed near the basal end. Only one spermatozoon fuse with the ovum completely and fertilises it. The process of fertilization takes place effectively only when the sperm reaches the ovum within its viable condition. It remains for two hours from its being exposed to naked otherwise it perishes. Moreover, the fertilized egg undergoes a number of steps such as cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation, encystation and hatching.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Some of the Hydra has both male and female reproductive organs and are known as hermaphrodites. Hydra has a tubular, radially symmetric body that extends up to 10 mm long, secured by a simple adhesive foot called the basal disc. A sticky fluid is secreted by gland cells present in the basal disc that accounts for its adhesive properties.
Complete answer: Cross fertilization occurs in Hydra. In Hydra, the testis matures earlier than the ovary. Testis releases mature sperm cells that swim in the water with the help of tail and through water, it reaches to the second Hydra. One of the sperm comes into contact with the ovum and fertilised female egg develops into a zygote. The body of the Hydra looks like a tube with tentacles arranged around the head pole of the organism. The reproductive structures of hydra consist of the testis (produce sperm cells) and the ovary (produces the egg) that are located under the ectoderm. The testis is formed near the oral end of the hydra while the ovaries formed near the basal end. Only one spermatozoon fuse with the ovum completely and fertilises it. The process of fertilization takes place effectively only when the sperm reaches the ovum within its viable condition. It remains for two hours from its being exposed to naked otherwise it perishes. Moreover, the fertilized egg undergoes a number of steps such as cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation, encystation and hatching.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Some of the Hydra has both male and female reproductive organs and are known as hermaphrodites. Hydra has a tubular, radially symmetric body that extends up to 10 mm long, secured by a simple adhesive foot called the basal disc. A sticky fluid is secreted by gland cells present in the basal disc that accounts for its adhesive properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




