
This is common in graphite and diamond:
A. Density
B. Crystal structure
C. Atomic weight
D. Electrical conductivity
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Graphite and diamond are both allotropes of carbon but have different properties.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define allotropes as different physical forms of a given element that exist in the same physical state. Here, we will discuss two allotropes of carbon which are graphite and diamond. We know that both the allotropes are made up of carbon atoms but still have different properties. Let’s discuss one by one:
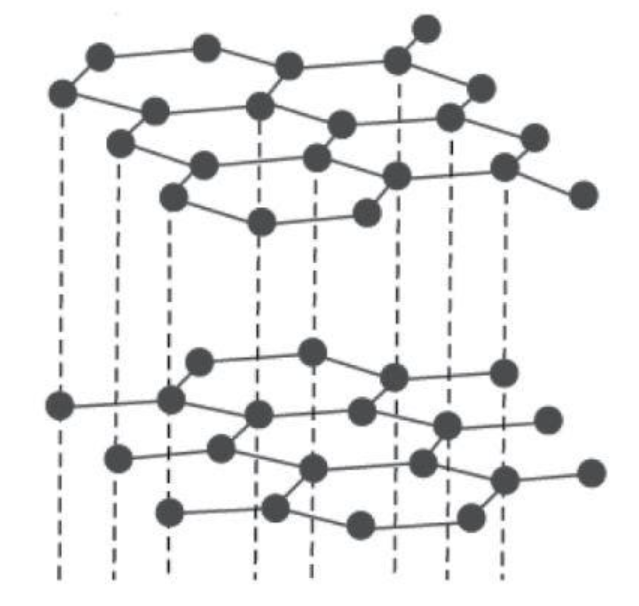
Graphite: It has a layered structure in which layers are hexagonal rings made up of carbon atoms. These layers are held by van der Waals forces which make it soft and slippery. In graphite, each carbon atom is connected to three carbons using its three valence electrons and giving the fourth for delocalization. The electronic mobility makes graphite a good conductor of electricity. The crystal structure can be shown as follows:
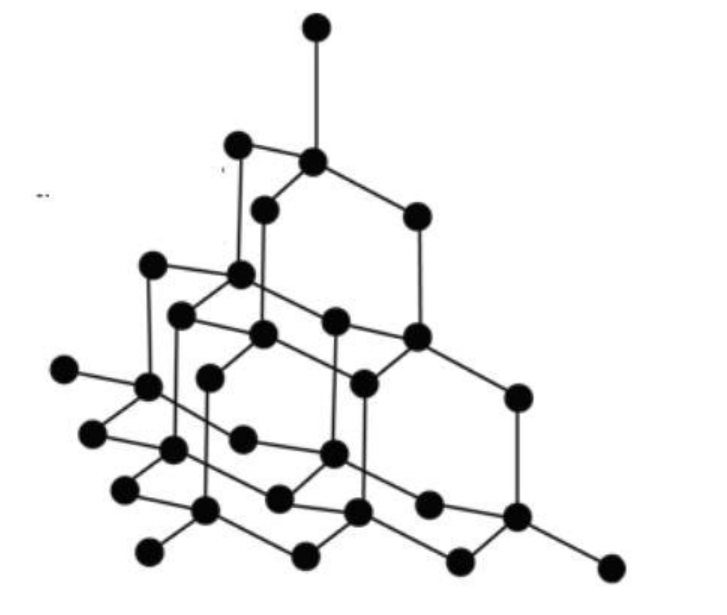
Diamond: We have crystal lattice for diamond. Here, each carbon atom is connected to four carbons using all of its valence electrons. So there are no delocalized electrons for electricity conduction. Its networking structure makes it the hardest substance. The crystal structure can be shown as follows:
From the above discussion, we can infer that crystal structure is different for graphite and diamond. Density being dependent on the crystal structure, packing efficiency would also differ for graphite and diamond. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity but the diamond isn’t. So, the only common characteristic is that both of them are made up of carbon atoms that have a definite atomic mass that doesn’t change with form.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
All the mentioned properties are structure-dependent except atomic weight. It is the same and fixed for a given element.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define allotropes as different physical forms of a given element that exist in the same physical state. Here, we will discuss two allotropes of carbon which are graphite and diamond. We know that both the allotropes are made up of carbon atoms but still have different properties. Let’s discuss one by one:
Graphite: It has a layered structure in which layers are hexagonal rings made up of carbon atoms. These layers are held by van der Waals forces which make it soft and slippery. In graphite, each carbon atom is connected to three carbons using its three valence electrons and giving the fourth for delocalization. The electronic mobility makes graphite a good conductor of electricity. The crystal structure can be shown as follows:

Diamond: We have crystal lattice for diamond. Here, each carbon atom is connected to four carbons using all of its valence electrons. So there are no delocalized electrons for electricity conduction. Its networking structure makes it the hardest substance. The crystal structure can be shown as follows:

From the above discussion, we can infer that crystal structure is different for graphite and diamond. Density being dependent on the crystal structure, packing efficiency would also differ for graphite and diamond. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity but the diamond isn’t. So, the only common characteristic is that both of them are made up of carbon atoms that have a definite atomic mass that doesn’t change with form.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
All the mentioned properties are structure-dependent except atomic weight. It is the same and fixed for a given element.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




