
Thickening of collenchyma is due to-
A. Lignin
B. Pectin
C. Suberin
D. None of above
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: It is a structural acidic heteropolysaccharide found in terrestrial plants' main and middle lamella and cell walls. Galacturonic acid, a galactose-derived sugar acid, is its key ingredient. Henri Braconnot first isolated it and described it in 1825.
Complete answer:
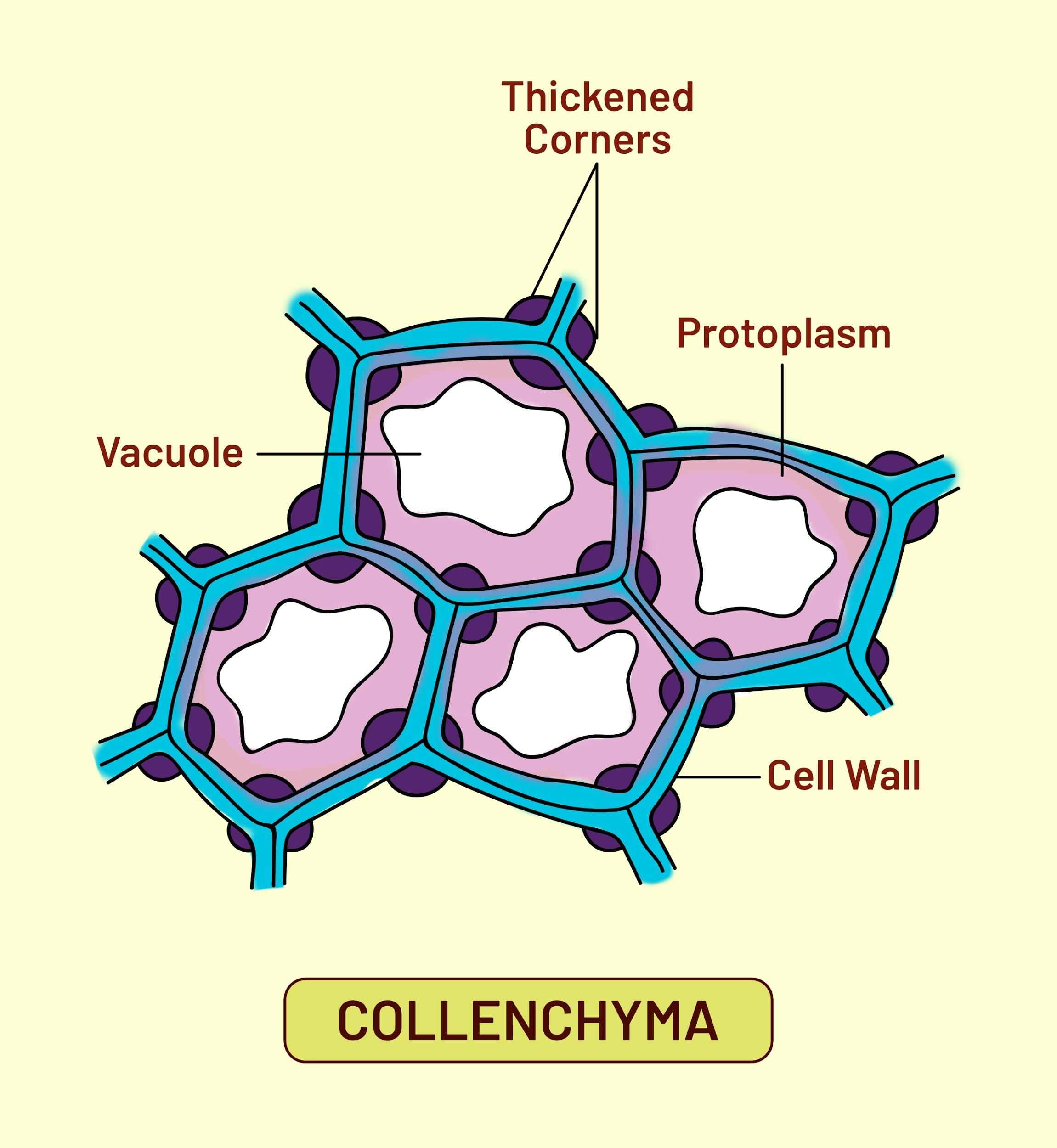
The tissue of Collenchyma is made up of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. In particular, in growing shoots and leaves, they provide structural support. The cells of Collenchyma normally live and have only a thick primary cell wall consisting of cellulose and pectin.
It is produced as a white to light brown powder commercially, mainly extracted from citrus fruits, and is used as a gelling agent in food, particularly in jams and jellies. It is also used as a stabiliser in fruit juices and milk drinks, and as a source of dietary fibre in cake fillings, medicines, and candy.
Additional Information: Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers which, in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae, form key structural materials. In the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, lignins are particularly important because they lend rigidity and do not easily rot.
Suberin is a lipophilic macromolecule found in specialised plant cell walls where the environment needs insulation or protection. The periderm, the tissue that envelops secondary stems as part of the bark, is produced by suberized cells, and grows after wounding or leaf abscission as the sealing tissue.
So, the correct answer is ‘pectin’.
Note: Pectin is an essential polysaccharide of the cell wall that enables extension of the primary cell wall and plant growth. Pectin is broken down by the enzymes pectinase and pectinesterase during fruit ripening, in which the fruit becomes softer when the middle lamellas break down and cells are isolated from each other.
Complete answer:
The tissue of Collenchyma is made up of elongated cells with irregularly thickened walls. In particular, in growing shoots and leaves, they provide structural support. The cells of Collenchyma normally live and have only a thick primary cell wall consisting of cellulose and pectin.
It is produced as a white to light brown powder commercially, mainly extracted from citrus fruits, and is used as a gelling agent in food, particularly in jams and jellies. It is also used as a stabiliser in fruit juices and milk drinks, and as a source of dietary fibre in cake fillings, medicines, and candy.

Additional Information: Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers which, in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae, form key structural materials. In the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, lignins are particularly important because they lend rigidity and do not easily rot.
Suberin is a lipophilic macromolecule found in specialised plant cell walls where the environment needs insulation or protection. The periderm, the tissue that envelops secondary stems as part of the bark, is produced by suberized cells, and grows after wounding or leaf abscission as the sealing tissue.
So, the correct answer is ‘pectin’.
Note: Pectin is an essential polysaccharide of the cell wall that enables extension of the primary cell wall and plant growth. Pectin is broken down by the enzymes pectinase and pectinesterase during fruit ripening, in which the fruit becomes softer when the middle lamellas break down and cells are isolated from each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




