
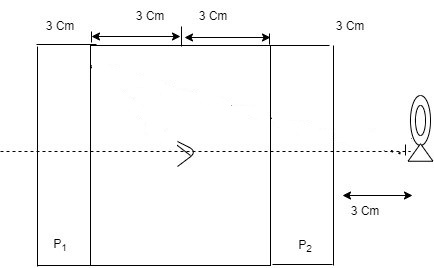
There is an insect inside a cabin eying towards a thick glass plate P1. Insect sees the images of light source across the glass plate P1 outside the cabin. The cabin is made of thick glass plates of refractive index $ \text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ =}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{2}} $ and thickness is 3cm. The insect is eying from the middle of the cabin as shown in the figure. (Glass plates are partially reflective and consider only parallel rays)
At what distance (from the eye of the insect) will the eye see the first image?

Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: The first image seen by the insect is due to the reflection of light from the surface of $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ after being refracted from the surface of $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ . Also considering the surface of $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ as a plane mirror which has a property that the distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of the object placed in front of it.
Complete step by step solution
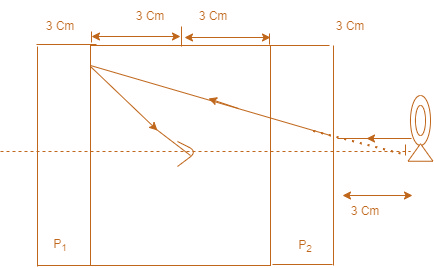
When the light from the source passes through $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ , it gets refracted from the glass surface forming a virtual source at a distance less than the actual distance from the glass plate. Now this refracted ray passes through air and gets reflected from the partially reflecting plate $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ forming an image in the eyes of the insect as shown in figure.
As a property of a plane mirror, the image is formed at the same distance from the mirror as the virtual object formed.
This is equal to:
$ \text{d=3}+\text{3}+\text{3}+\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ }} $
Here $ \text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ } $ is the refractive index of glass plate $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ from which refraction has taken place
$ \text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{3}{2} $
So
$ =9+\dfrac{3}{3}\times 2 $
$ =9+2 $
$ \text{d}=11\text{ cm} $
Now the image is formed $ 11\text{ cm} $ behind the plate $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $
Distance of image from insect $ =3+11=14\text{ cm} $
$ \therefore $ First image can be seen by the insect is at $ 14\text{ cm} $ .
Note
Here we have ignored the reflections caused by $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ and refraction caused by $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ as they are not required to solve the question despite of their occurrence. Reflection and refraction plays an important role in our daily life. A very important application of refraction of light in astronomy is stars appear to twinkle on a clear sky. Common examples of reflection include reflection of light, sound and water waves.
Complete step by step solution

When the light from the source passes through $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ , it gets refracted from the glass surface forming a virtual source at a distance less than the actual distance from the glass plate. Now this refracted ray passes through air and gets reflected from the partially reflecting plate $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ forming an image in the eyes of the insect as shown in figure.
As a property of a plane mirror, the image is formed at the same distance from the mirror as the virtual object formed.
This is equal to:
$ \text{d=3}+\text{3}+\text{3}+\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ }} $
Here $ \text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ } $ is the refractive index of glass plate $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ from which refraction has taken place
$ \text{ }\!\!\mu\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{3}{2} $
So
$ =9+\dfrac{3}{3}\times 2 $
$ =9+2 $
$ \text{d}=11\text{ cm} $
Now the image is formed $ 11\text{ cm} $ behind the plate $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $
Distance of image from insect $ =3+11=14\text{ cm} $
$ \therefore $ First image can be seen by the insect is at $ 14\text{ cm} $ .
Note
Here we have ignored the reflections caused by $ {{\text{P}}_{2}} $ and refraction caused by $ {{\text{P}}_{1}} $ as they are not required to solve the question despite of their occurrence. Reflection and refraction plays an important role in our daily life. A very important application of refraction of light in astronomy is stars appear to twinkle on a clear sky. Common examples of reflection include reflection of light, sound and water waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




