
There is a small island in the middle of a 100 m wide river and a tall tree stands on the island. P and Q are points directly opposite to each other on two banks and in the line with the tree. If the angle of elevation of the top of the tree from P and Q are respectively ${30^ \circ }$ and ${45^ \circ }$. Find the height of the tree.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:
We will begin by drawing 2 right triangles. From the two triangles, find the trigonometric ratios involving the height of the tree and the distance from its base to the point. Then, solve the equations to find the height of the tree.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given statement, we have the condition as shown in the figure below.
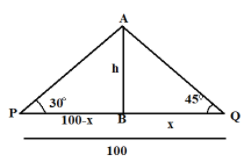
There are two points P an Q and the distance between them be 100m
Let $AB = h$ be the height of the tree.
Let the distance from the base of the tree $B$ to the point Q be $x$, then the distance from point P to the base of tree will be $100 - x$
Consider triangle, $ABQ$
$\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BQ}}$
We know that $\tan {45^ \circ } = 1$
On substituting the known values, we will get,
$
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{h}{x} \\
\Rightarrow x = h \\
$
Consider triangle $ABP$
$\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{h}{{100 - x}}$
We know that $\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and $x = h$
On substituting the known values, we will get,
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{100 - h}} \\
\Rightarrow 100 - h = h\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow h\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) = 100 \\
$
Divide both sides by \[\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\]
$h = \dfrac{{100}}{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}$
Hence, the height of the tree is $\dfrac{{100}}{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}$ metres.
Note:
In these types of questions, diagrams play an important role as it helps to understand the question in a better way. Students must know all the trigonometric ratios for this type of question. here, we have used tangent ratio and $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$
We will begin by drawing 2 right triangles. From the two triangles, find the trigonometric ratios involving the height of the tree and the distance from its base to the point. Then, solve the equations to find the height of the tree.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given statement, we have the condition as shown in the figure below.

There are two points P an Q and the distance between them be 100m
Let $AB = h$ be the height of the tree.
Let the distance from the base of the tree $B$ to the point Q be $x$, then the distance from point P to the base of tree will be $100 - x$
Consider triangle, $ABQ$
$\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BQ}}$
We know that $\tan {45^ \circ } = 1$
On substituting the known values, we will get,
$
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{h}{x} \\
\Rightarrow x = h \\
$
Consider triangle $ABP$
$\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{h}{{100 - x}}$
We know that $\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ and $x = h$
On substituting the known values, we will get,
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{100 - h}} \\
\Rightarrow 100 - h = h\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow h\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) = 100 \\
$
Divide both sides by \[\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\]
$h = \dfrac{{100}}{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}$
Hence, the height of the tree is $\dfrac{{100}}{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}$ metres.
Note:
In these types of questions, diagrams play an important role as it helps to understand the question in a better way. Students must know all the trigonometric ratios for this type of question. here, we have used tangent ratio and $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




