
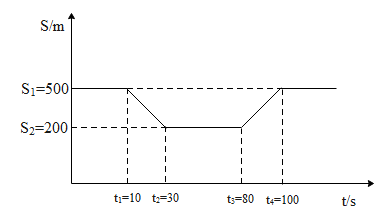
There is a narrow bridge somewhere on the roads connecting two towns. Two cars travel from one of the towns to the other with a constant speed ${{v}_{1}}$ everywhere on the road except the bridge, where they travel with another constant speed ${{v}_{2}}$ . How the separation between the cars varies with time t is shown in the following graph. What is the speed ${{v}_{1}}$ of the cars on the road.

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: In the above question the variation of the separation (s) between the two cars with time is given in the graph. To determine the speed of the cars ${{v}_{1}}$ we will consider any one of the cars. Then with respect to one of the cars the obtained velocity will be equal to the velocity ${{v}_{1}}$ of the either cars on the road.
Formula used:
$s=\dfrac{d}{t}$
Complete answer:
Let us say a body covers distance ‘d’ in time ‘t’. Then the speed ‘s’ of the body is given by
$s=\dfrac{d}{t}$
In the above graph let us say there are two cars car ‘A’ and car ‘B’ such that A is ahead of B. Before time interval of 10 sec the distance of separation between the two cars is 500m As soon as the car ‘A’ reaches the bridge its speed changes. Hence the distance of separation after 10 sec decreases. Further when the car B reaches the bridge the speed of the car decreases and hence after 30 sec the distance of separation between the two remains constant. Therefore when the car ‘B’ is on the road at a distance of d = 500m (such that the car ‘A’ enters the bridge) it takes a time interval 20sec for the car ‘B’ to cover that distance and reach the bridge. Hence the speed of the car on the road,
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{500}{30-10}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{500}{30-10}m/s=\dfrac{500}{20}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=25m/s \\
\end{align}$
Note:
The above problem can also be solved with respect to car A. When the car ‘A’ exits the bridge the distance of separation will keep on increasing. When finally the car ‘B’ also exits the bridge the distance of separation will be constant. Hence accordingly from the graph the speed of the wither cars on the road can be determined.
Formula used:
$s=\dfrac{d}{t}$
Complete answer:
Let us say a body covers distance ‘d’ in time ‘t’. Then the speed ‘s’ of the body is given by
$s=\dfrac{d}{t}$
In the above graph let us say there are two cars car ‘A’ and car ‘B’ such that A is ahead of B. Before time interval of 10 sec the distance of separation between the two cars is 500m As soon as the car ‘A’ reaches the bridge its speed changes. Hence the distance of separation after 10 sec decreases. Further when the car B reaches the bridge the speed of the car decreases and hence after 30 sec the distance of separation between the two remains constant. Therefore when the car ‘B’ is on the road at a distance of d = 500m (such that the car ‘A’ enters the bridge) it takes a time interval 20sec for the car ‘B’ to cover that distance and reach the bridge. Hence the speed of the car on the road,
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{d}{{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{500}{30-10}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=\dfrac{500}{30-10}m/s=\dfrac{500}{20}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=25m/s \\
\end{align}$
Note:
The above problem can also be solved with respect to car A. When the car ‘A’ exits the bridge the distance of separation will keep on increasing. When finally the car ‘B’ also exits the bridge the distance of separation will be constant. Hence accordingly from the graph the speed of the wither cars on the road can be determined.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




