
There is a depression in the surface of the liquid in a capillary when:
A. The cohesive force is smaller than the adhesive force
B. The cohesive force is greater than the adhesive force
C. The cohesive and adhesive forces are equal
D. None of the above is true
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without any opposition of external forces, like gravity, is known as capillary. This effect occurs due to the intermolecular forces between the liquid and surrounding surface.
Complete step by step answer:
In a capillary action, the molecules of the liquid attract each other. This is due to the force of cohesion between the molecules. And the molecules of the liquid also get attracted towards the walls of the container. This is known as the adhesion force.
Now, we know that the water molecules are getting attracted to the molecules of the walls of the container and at the same time, the molecules of liquid are forced to remain together (this is due to the forces mentioned above). Now, when the molecules of the liquid stick to the walls of the container and the other molecules get stuck to the molecule touching the glass, then the formation of meniscus occurs.
The meniscus is generally of two types that are concave meniscus and the convex meniscus. When the molecules of the liquid are more attracted towards the walls of the container then a concave meniscus is formed whereas a convex meniscus is formed when the molecules of the liquid have a stronger attraction towards each other than to the container.
Now, the depression in the surface of the liquid in the capillary means that the liquid is forming a concave meniscus. This is also shown in the diagram given below:
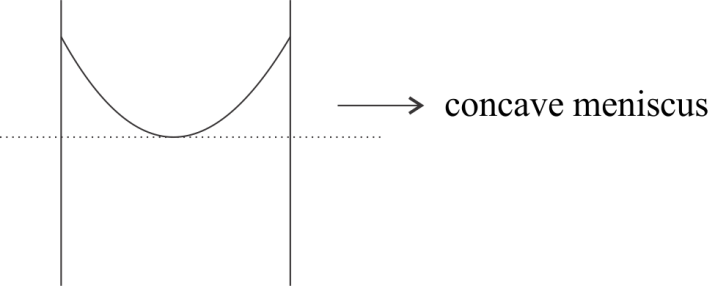
Hence, from the above discussion we can say that the concave meniscus is formed when the molecules of liquid are attracted more towards the walls of the container that is when the adhesion force is greater than the cohesion force.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The examples of the liquids which form a convex and a concave meniscus are mercury and water respectively. In mercury the adhesive forces are smaller than that of the cohesive forces and in water the cohesive forces are smaller than the adhesive forces.
Complete step by step answer:
In a capillary action, the molecules of the liquid attract each other. This is due to the force of cohesion between the molecules. And the molecules of the liquid also get attracted towards the walls of the container. This is known as the adhesion force.
Now, we know that the water molecules are getting attracted to the molecules of the walls of the container and at the same time, the molecules of liquid are forced to remain together (this is due to the forces mentioned above). Now, when the molecules of the liquid stick to the walls of the container and the other molecules get stuck to the molecule touching the glass, then the formation of meniscus occurs.
The meniscus is generally of two types that are concave meniscus and the convex meniscus. When the molecules of the liquid are more attracted towards the walls of the container then a concave meniscus is formed whereas a convex meniscus is formed when the molecules of the liquid have a stronger attraction towards each other than to the container.
Now, the depression in the surface of the liquid in the capillary means that the liquid is forming a concave meniscus. This is also shown in the diagram given below:

Hence, from the above discussion we can say that the concave meniscus is formed when the molecules of liquid are attracted more towards the walls of the container that is when the adhesion force is greater than the cohesion force.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The examples of the liquids which form a convex and a concave meniscus are mercury and water respectively. In mercury the adhesive forces are smaller than that of the cohesive forces and in water the cohesive forces are smaller than the adhesive forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




