
There exist an equilibrium between solid $ SrS{{O}_{4}} $ , $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ and $ SO_{4}^{2-} $ ion in aqueous medium. The possible equilibrium states are shown in the figure as a thick line. Now, if equilibrium is disturbed by addition of (a) $ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ and (b) $ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $ and dotted line represent approach of system towards equilibrium. Match the columns given below:
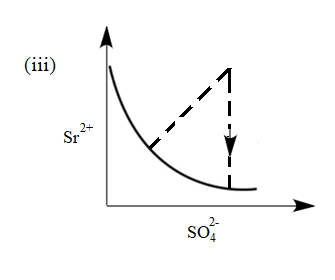
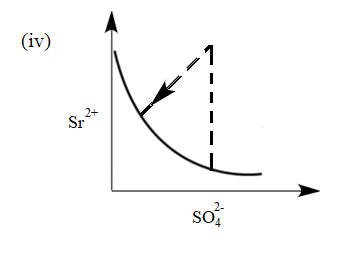
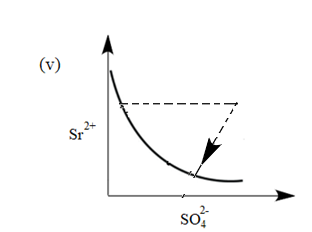
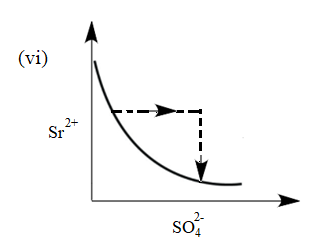
(I) Addition of $ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ (II) Addition of $ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $
(a) (I) (iii), (II) (iv)
(b) (I) (iv), (II) (v)
(c) (I) (vi), (II) (v)
(d) (I) (iv), (II) (vi)




Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint:
Common ion effect: It is the effect which describes the situation in which the compounds are added in an equilibrium system which have common ions that are already part of the system. It works under Le-Chatelier's principle that if a common ion is added to a system, then a shift in equilibrium will be observed.
Complete answer:
Whenever a system or a solution that consists of ionic compounds come in contact with other ionic compounds having a common ion, there is increase in the concentration of that specific ion and due to this, decrease in the solubility of ionic substance is observed. This phenomenon is termed as a common ion effect and it plays a significant role in the environmental and pharmaceutical industries.
Now, let us consider each case separately as follows:
(a) Addition of $ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ :
$ SrS{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ SrS{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+SO_{4}^{2-} $
$ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+2N{{O}_{3}}^{-} $
The common ion in the system is $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ . Therefore, In the system, an increase in the concentration of $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ ions will take place. Due to this equilibrium will shift towards the $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ . Hence the graph will be as follows:
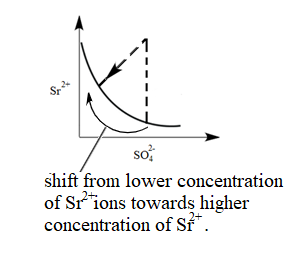
Therefore, (I) matches with graph (iv).
(b) Addition of $ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $ :
$ SrS{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ SrS{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+SO_{4}^{2-} $
$ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons 2{{K}^{+}}+S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $
The common ion in the system is $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ . Therefore, In the system, an increase in the concentration of $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ ions will take place. Due to this equilibrium will shift towards $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ . Hence the graph will be as follows:
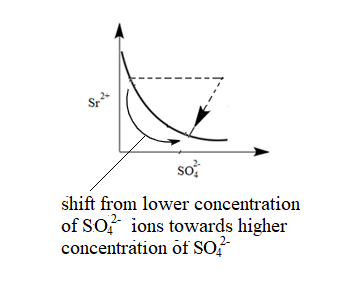
Therefore, (II) matches with graph (v).
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that, when a common ion is added to the system then faster it will react and therefore a decrease in the concentration of the counterion is observed. Hence in each graph, with the increase in the concentration of common ions, a decrease in concentration of counterion is also indicated.
Common ion effect: It is the effect which describes the situation in which the compounds are added in an equilibrium system which have common ions that are already part of the system. It works under Le-Chatelier's principle that if a common ion is added to a system, then a shift in equilibrium will be observed.
Complete answer:
Whenever a system or a solution that consists of ionic compounds come in contact with other ionic compounds having a common ion, there is increase in the concentration of that specific ion and due to this, decrease in the solubility of ionic substance is observed. This phenomenon is termed as a common ion effect and it plays a significant role in the environmental and pharmaceutical industries.
Now, let us consider each case separately as follows:
(a) Addition of $ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ :
$ SrS{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ SrS{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+SO_{4}^{2-} $
$ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ Sr{{(N{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+2N{{O}_{3}}^{-} $
The common ion in the system is $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ . Therefore, In the system, an increase in the concentration of $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ ions will take place. Due to this equilibrium will shift towards the $ S{{r}^{2+}} $ . Hence the graph will be as follows:

Therefore, (I) matches with graph (iv).
(b) Addition of $ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $ :
$ SrS{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ SrS{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons S{{r}^{2+}}+SO_{4}^{2-} $
$ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} $ dissociates as follows:
$ {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons 2{{K}^{+}}+S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $
The common ion in the system is $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ . Therefore, In the system, an increase in the concentration of $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ ions will take place. Due to this equilibrium will shift towards $ S{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ . Hence the graph will be as follows:

Therefore, (II) matches with graph (v).
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that, when a common ion is added to the system then faster it will react and therefore a decrease in the concentration of the counterion is observed. Hence in each graph, with the increase in the concentration of common ions, a decrease in concentration of counterion is also indicated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




