
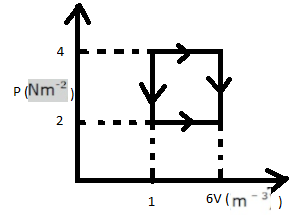
The work done in taking an ideal gas through one cycle of operation as shown in the indicated diagram:
A. ${10^{ - 5}}\,J$
B. ${10^{ - 3}}\,J$
C. ${10^{ - 2}}\,J$
D. $10\,J$

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint:
Gases may expand or contract under a certain constraint (e.g. pressure); the final state of the gas may vary based on the form of constraint. For instance, in a different state than a gas that expands while pressure remains constant (called isobaric process), an ideal gas that expands while its temperature is held constant (called isothermal process) can occur. The isobaric mechanism and associated concepts are discussed below.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let us see what isobaric process is-
A thermodynamic process is an isobaric process in which pressure remains constant $\Delta P = 0$ . For an ideal gas, this suggests that a gas’s volume is equal to its temperature. Let’s assume a case where, at constant $P$, a gas acts on a piston. The force exerted is constant since the friction is constant, and the work performed is given as
$W = Fd$
where $F = PA$ is the force imposed by the friction on the piston.
The work done by the gas is-
$W = PAd$
Since, a cylinder’s change in volume is its cross-sectional area $A$ times the displacement $d$ , the volume change is given by $Ad = V$
Hence, $W = P\Delta V$
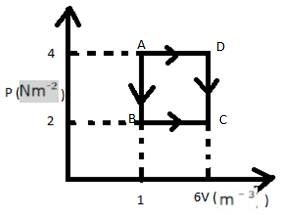
Now, let us consider the rectangle ABCD-
Work done = Area of ABCD
= $AB \times BC$
= $(4 - 2) \times (6 - 1)$
= $10\,J$
The work done in taking an ideal gas through one cycle of operation as shown in the indicator diagram is $10\,Joule$ .
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Here we have to observe the diagram and consider the triangle ABCD. Also for an isobaric process if $\Delta V$ is positive, work done is also positive, which implies the gas functions in the outside world.
Gases may expand or contract under a certain constraint (e.g. pressure); the final state of the gas may vary based on the form of constraint. For instance, in a different state than a gas that expands while pressure remains constant (called isobaric process), an ideal gas that expands while its temperature is held constant (called isothermal process) can occur. The isobaric mechanism and associated concepts are discussed below.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let us see what isobaric process is-
A thermodynamic process is an isobaric process in which pressure remains constant $\Delta P = 0$ . For an ideal gas, this suggests that a gas’s volume is equal to its temperature. Let’s assume a case where, at constant $P$, a gas acts on a piston. The force exerted is constant since the friction is constant, and the work performed is given as
$W = Fd$
where $F = PA$ is the force imposed by the friction on the piston.
The work done by the gas is-
$W = PAd$
Since, a cylinder’s change in volume is its cross-sectional area $A$ times the displacement $d$ , the volume change is given by $Ad = V$
Hence, $W = P\Delta V$

Now, let us consider the rectangle ABCD-
Work done = Area of ABCD
= $AB \times BC$
= $(4 - 2) \times (6 - 1)$
= $10\,J$
The work done in taking an ideal gas through one cycle of operation as shown in the indicator diagram is $10\,Joule$ .
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Here we have to observe the diagram and consider the triangle ABCD. Also for an isobaric process if $\Delta V$ is positive, work done is also positive, which implies the gas functions in the outside world.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




