
The work done in slowly pulling up a block of wood weighing \[2{\text{ KN}}\] for a length of \[10{\text{ m}}\] on a smooth plane inclined at an angle of \[{15^ \circ }\] with the horizontal by a force parallel to the incline is? \[\left( {\cos {{15}^ \circ } = 0.96{\text{ }}\sin {{15}^ \circ } = 0.26} \right)\]
A. \[{\text{4}}{\text{.36 KJ}}\]
B. \[{\text{5}}{\text{.17 KJ}}\]
C. \[{\text{8}}{\text{.91 KJ}}\]
D. \[{\text{9}}{\text{.82 KJ}}\]
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to find out the work done in slowly pulling up a block on a smooth inclined plane. As gravity will resist the block from moving upwards, we need to apply a force equal to the force of gravity in the inclined plane direction. To find out the work done multiply the force component along the direction of displacement with displacement.
\[{\text{W = FScos}}\theta \](For constant force)
Where, \[F = \] Constant force applied
\[S = \] Displacement
\[\theta = \] angle between \[{\text{F}}\]and \[{\text{S}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Weight of block \[mg = 2000{\text{ N}}\]
Displacement of the block on the smooth inclined plane, \[S = 10{\text{ m}}\]
Angle of the inclined plane is \[\theta {\text{ = 1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ }\]
Let force \[F\] be applied parallel to the incline to pull the block upwards
We need to find out the work done \[W\] in pulling the block up the inclined surface
The force of gravity offers a resisting force while pulling up the block
We can resolve the force of gravity in two components:
\[mg\sin \theta \] which acting along the incline and \[{\text{mgcos}}\theta \] which is acting perpendicular to the incline
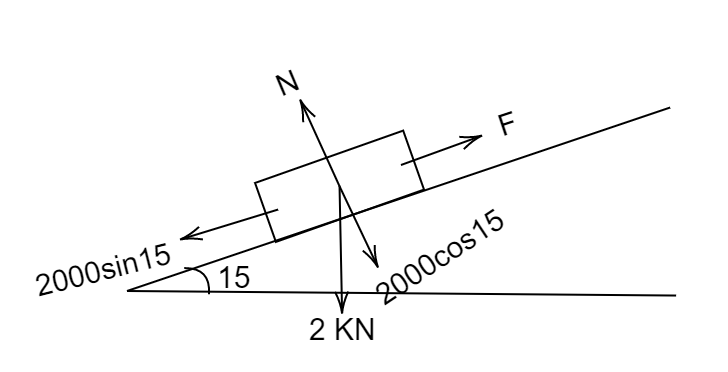
Thus, the force applied must be equal to the force of gravity along the incline to pull the block up
\[F = mg\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 2000\sin {15^ \circ }\]
The normal force due to the incline must be equal to \[{\text{mgcos}}\theta \] to maintain equilibrium in the perpendicular direction of incline
\[{\text{N = mgcos}}\theta \Rightarrow {\text{2000cos1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ }\]
To find out the work done we use the formula,
\[{\text{W = F}} \cdot {\text{S = FScos}}\theta \]
Force \[F = 2000\sin {15^ \circ }\] is along the same direction as the displacement of the block
Thus, \[{\text{W = 2000sin1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ } \times 10\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{W = 520}} \times {\text{10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{W = 5200J}} \Rightarrow {\text{5}}{\text{.2KJ}}\]
Thus, work done in pulling the block upward is \[{\text{5}}{\text{.2KJ}}\]
Therefore B. is the correct option.
Note:
The formula \[{\text{W = FScos}}\theta \] is applicable only when the force given is constant and applied in a particular direction if the force is varying in magnitude, we cannot use dot product to find out the work done instead we need to integrate the force over the range of displacement to find out the work done. In that case work done, \[W = \int\limits_{{s_1}}^{{s_2}} {dW} = \int\limits_{{s_1}}^{{s_2}} {F \cdot ds} \]
Where, \[F = \] Constant force applied
\[S = \] Displacement
\[\theta = \] angle between \[{\text{F}}\]and \[{\text{S}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Weight of block \[mg = 2000{\text{ N}}\]
Displacement of the block on the smooth inclined plane, \[S = 10{\text{ m}}\]
Angle of the inclined plane is \[\theta {\text{ = 1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ }\]
Let force \[F\] be applied parallel to the incline to pull the block upwards
We need to find out the work done \[W\] in pulling the block up the inclined surface
The force of gravity offers a resisting force while pulling up the block
We can resolve the force of gravity in two components:
\[mg\sin \theta \] which acting along the incline and \[{\text{mgcos}}\theta \] which is acting perpendicular to the incline

Thus, the force applied must be equal to the force of gravity along the incline to pull the block up
\[F = mg\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 2000\sin {15^ \circ }\]
The normal force due to the incline must be equal to \[{\text{mgcos}}\theta \] to maintain equilibrium in the perpendicular direction of incline
\[{\text{N = mgcos}}\theta \Rightarrow {\text{2000cos1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ }\]
To find out the work done we use the formula,
\[{\text{W = F}} \cdot {\text{S = FScos}}\theta \]
Force \[F = 2000\sin {15^ \circ }\] is along the same direction as the displacement of the block
Thus, \[{\text{W = 2000sin1}}{{\text{5}}^ \circ } \times 10\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{W = 520}} \times {\text{10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{W = 5200J}} \Rightarrow {\text{5}}{\text{.2KJ}}\]
Thus, work done in pulling the block upward is \[{\text{5}}{\text{.2KJ}}\]
Therefore B. is the correct option.
Note:
The formula \[{\text{W = FScos}}\theta \] is applicable only when the force given is constant and applied in a particular direction if the force is varying in magnitude, we cannot use dot product to find out the work done instead we need to integrate the force over the range of displacement to find out the work done. In that case work done, \[W = \int\limits_{{s_1}}^{{s_2}} {dW} = \int\limits_{{s_1}}^{{s_2}} {F \cdot ds} \]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




