
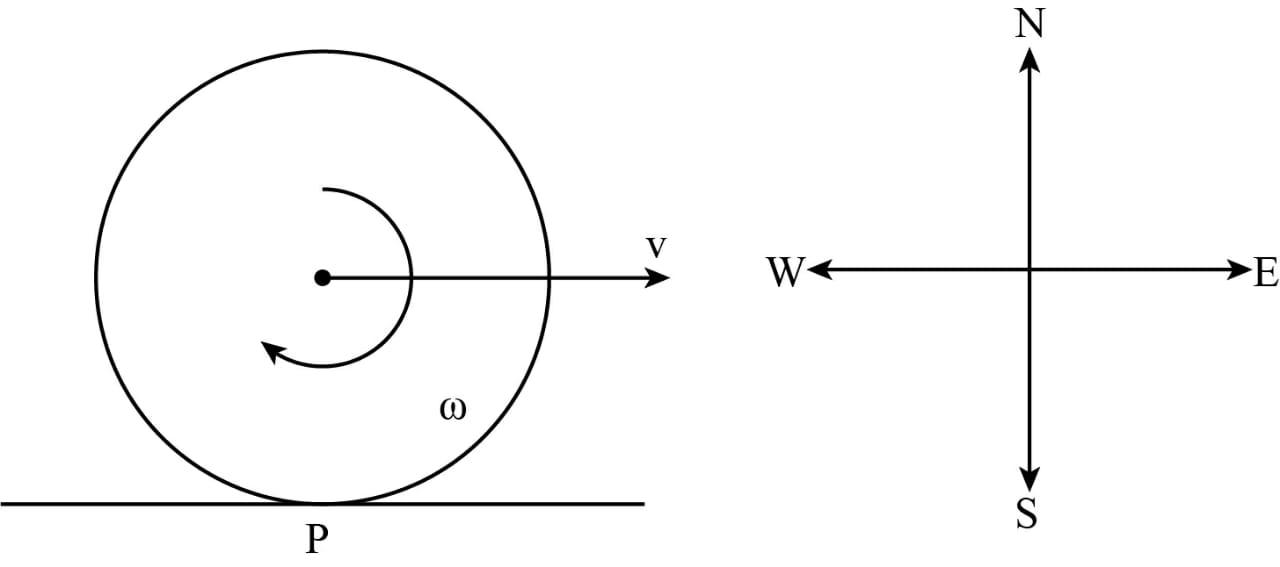
The wheels of an airplane are set into the rotation just before landing so that the wheels do not slip on the ground. If the airplane is traveling in the east direction, what should be the direction of the angular velocity vector of the wheels?
A. East
B. West
C. South
D. North
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Angular velocity vector has no component along with the wheel. When the wheel is spinning, it has not only an angular speed but also a direction. The size of angular velocity tells you about the angular speed and direction of the vector to determine the axis of rotation, whether it is clockwise or anticlockwise.
Complete step by step answer:
We know angular velocity $\left( \omega \right)$ refers to how fast an object rotates or revolves relative to another, i.e., how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time. It is of two types, i.e., orbital angular velocity and spin angular velocity.
The formula used to find the angular velocity-
$\therefore \omega = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}$ Where $\theta $ the angle and t is is the time.
The wheel is spinning; therefore, the tangential (linear) velocity at any point on the wheel is constantly changing direction — except for at the very center point of the wheel, where the base of the angular velocity vector sits. If the wheel is lying flat on the ground, the vector’s head points up or down, away from the wheel, depending on which direction the wheel is rotating. So the rolling point at rest and rotation should be clockwise. Therefore the direction of angular velocity is north.
Note: You can use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the angular velocity vector. Wrap your right hand around the wheel so that your fingers point in the direction of the tangential motion at any point — the fingers on your right hand should go in the same direction as the wheel’s rotation when you wrap your right hand around the wheel, your thumb points in the direction of the angular velocity vector.
Complete step by step answer:
We know angular velocity $\left( \omega \right)$ refers to how fast an object rotates or revolves relative to another, i.e., how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time. It is of two types, i.e., orbital angular velocity and spin angular velocity.
The formula used to find the angular velocity-

$\therefore \omega = \dfrac{{\Delta \theta }}{{\Delta t}}$ Where $\theta $ the angle and t is is the time.
The wheel is spinning; therefore, the tangential (linear) velocity at any point on the wheel is constantly changing direction — except for at the very center point of the wheel, where the base of the angular velocity vector sits. If the wheel is lying flat on the ground, the vector’s head points up or down, away from the wheel, depending on which direction the wheel is rotating. So the rolling point at rest and rotation should be clockwise. Therefore the direction of angular velocity is north.
Note: You can use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the angular velocity vector. Wrap your right hand around the wheel so that your fingers point in the direction of the tangential motion at any point — the fingers on your right hand should go in the same direction as the wheel’s rotation when you wrap your right hand around the wheel, your thumb points in the direction of the angular velocity vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




