
The wheat grain is a:
A. Fruit
B. Seed
C. Embryo
D. Glume
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint:-
Before answering this question, we must be well aware of the structure of the monocot seed. Also, we must know that fruit and the seeds are two different parts but sometimes, they may be fused to look like a single part.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
Wheat(Triticum aestivum) belongs to the modern grass family i.e. Gramineae or Poaceae.
As per the classification, fruits are divided into three categories:
Simple fruits: Produced from one flower and multicarpellary or monocarpellary syncarpous ovary.
Aggregate fruits: Produced from one flower and bicarpellary to multicarpellary ovary but ovary is always apocarpous.
Composite fruits: Produced from entire inflorescence.
Simple fruit is further classified into:
Fleshy/Pulpy fruit.
Dry fruits.
Dry fruits have three subdivisions:
Indehiscent dry fruits
Dehiscent dry fruits
Schizocarpic dry fruits
Indehiscent dry fruits:
- Cypsela: Sunflower, Marigold.
- Caryopsis: These are small, one seeded dry fruits, which develop from monocarpellary, superior ovary. In these fruits, Pericarp is fused with the seed coat and forms a joint surface. Examples: Wheat, Rice, Maize, etc.
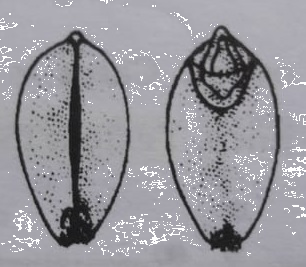
Figure: Caryopsis of Wheat.
-Achene: Clematis, Mirabilis, etc.
- Nut: Trapa, litchi.
- Samara: Holoptelia.
So the correct option is (a)Fruit.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Some edible parts of fruits:
a. Caryopsis: Whole fruit.
b. Coconut: Endosperm.
c. Water melon: Mesocarp, Endocarp and seeds.
d. Peanut: Cotyledons.
e. Cashew: Cotyledon and peduncle.
Note:-
- On the first glimpse, the wheat grain can look like seed but it is not.
- Many may think, as wheat is monocot so the wheat grain must be endosperm but it's not endosperm or seed it is an indehiscent fruit : Caryopsis.
Before answering this question, we must be well aware of the structure of the monocot seed. Also, we must know that fruit and the seeds are two different parts but sometimes, they may be fused to look like a single part.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
Wheat(Triticum aestivum) belongs to the modern grass family i.e. Gramineae or Poaceae.
As per the classification, fruits are divided into three categories:
Simple fruits: Produced from one flower and multicarpellary or monocarpellary syncarpous ovary.
Aggregate fruits: Produced from one flower and bicarpellary to multicarpellary ovary but ovary is always apocarpous.
Composite fruits: Produced from entire inflorescence.
Simple fruit is further classified into:
Fleshy/Pulpy fruit.
Dry fruits.
Dry fruits have three subdivisions:
Indehiscent dry fruits
Dehiscent dry fruits
Schizocarpic dry fruits
Indehiscent dry fruits:
- Cypsela: Sunflower, Marigold.
- Caryopsis: These are small, one seeded dry fruits, which develop from monocarpellary, superior ovary. In these fruits, Pericarp is fused with the seed coat and forms a joint surface. Examples: Wheat, Rice, Maize, etc.

Figure: Caryopsis of Wheat.
-Achene: Clematis, Mirabilis, etc.
- Nut: Trapa, litchi.
- Samara: Holoptelia.
So the correct option is (a)Fruit.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Some edible parts of fruits:
a. Caryopsis: Whole fruit.
b. Coconut: Endosperm.
c. Water melon: Mesocarp, Endocarp and seeds.
d. Peanut: Cotyledons.
e. Cashew: Cotyledon and peduncle.
Note:-
- On the first glimpse, the wheat grain can look like seed but it is not.
- Many may think, as wheat is monocot so the wheat grain must be endosperm but it's not endosperm or seed it is an indehiscent fruit : Caryopsis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




