
The wavelength of visible light is:
A. 200nm-370nm
B. 780nm-890nm
C. 380nm-760nm
D. 900nm-2000nm
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint- As we know, Wavelength of light is designated as the distance between the two successive crests of the light wave. Therefore, we simply say the distance between either one crest or trough of one wave and the next wave is called wavelength. And It is denoted by the letter lambda (λ).
Complete step-by-step answer:
Mathematically, wavelength of light calculated:
As light has the properties of a wave as well as particle, it can be expressed as:
$c = \lambda f$
Where, c- speed of light
$\lambda $- wavelength of the light.
$f$- the frequency of the light.
The wavelength for various colours of the visible range of spectrum of light is provided in the below table underneath.
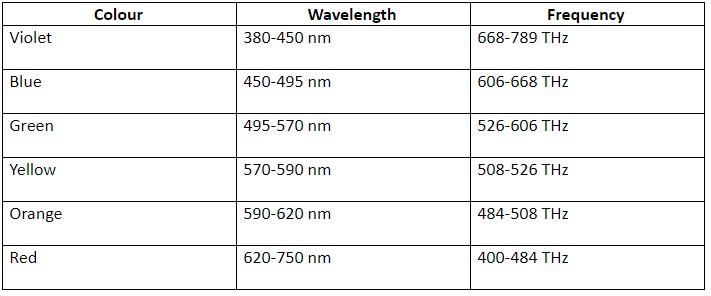
Typically, it’s 400nm to 700nm (Violet to Red) but we have some sensitivity to UV below 400nm (about 10 to 20nm I think) and some sensitivity to IR above 700nm - up to around 1350nm. After that, we might still have sensitivity, but the resultant energy from the light would damage our eyes rather than be simply detected.
Therefore, roughly it is from 400nm to 750 nm. The lens in your eye absorbs below 400 nm. In days before the use of lens inserts, people could see down to 350 nm after cataract surgery (removal of the natural lens). The long wave limit is not sharp and you might see something out near 800nm.
Note- Remember always, We can see that visible spectrum have wavelength range of 400nm to 700nm but in Angstrom we can also say 4000 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$to 7000 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$. And where 1 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$ is equal to 0.1 nanometers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Mathematically, wavelength of light calculated:
As light has the properties of a wave as well as particle, it can be expressed as:
$c = \lambda f$
Where, c- speed of light
$\lambda $- wavelength of the light.
$f$- the frequency of the light.
The wavelength for various colours of the visible range of spectrum of light is provided in the below table underneath.

Typically, it’s 400nm to 700nm (Violet to Red) but we have some sensitivity to UV below 400nm (about 10 to 20nm I think) and some sensitivity to IR above 700nm - up to around 1350nm. After that, we might still have sensitivity, but the resultant energy from the light would damage our eyes rather than be simply detected.
Therefore, roughly it is from 400nm to 750 nm. The lens in your eye absorbs below 400 nm. In days before the use of lens inserts, people could see down to 350 nm after cataract surgery (removal of the natural lens). The long wave limit is not sharp and you might see something out near 800nm.
Note- Remember always, We can see that visible spectrum have wavelength range of 400nm to 700nm but in Angstrom we can also say 4000 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$to 7000 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$. And where 1 ${{\text{A}}^{\text{0}}}$ is equal to 0.1 nanometers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




