
The vertices of the triangle are (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (1, -3). Is the triangle equilateral, isosceles or scalene?
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: We know the definition of equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle and scalene triangle. In equilateral triangles all the sides are equal. In the isosceles triangle only two sides are equal. In the scalene triangle no equal sides. By finding the distances of each said we will tell whether a given triangle is equilateral, isosceles or scalene.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given vertices are (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (1,-3).
We know that the distance between two points \[({x_1},{y_1})\] and \[({x_2},{y_2})\] is \[ = \sqrt {{{({x_1} - {x_2})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] .
Assume the diagram (for better understanding).
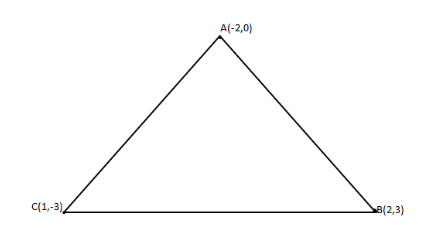
Now we find the distances of AB, AB and BC.
Now, the distance \[AB\] is given by,
The vertices of A and B are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2,0)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (2,3)\]
Substituting we get,
\[AB = \sqrt {{{( - 2 - 2)}^2} + {{(0 - 3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{( - 4)}^2} + {{( - 3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {16 + 9} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25} \]
\[ = 5\] units
Now, the distance of \[BC\] is given by,
The vertices of B and C are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = (2,3)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (1, - 3)\] .
\[BC = \sqrt {{{(2 - 1)}^2} + {{(3 - ( - 3))}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{(1)}^2} + {{(6)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {1 + 36} \]
\[ = \sqrt {37} \] units.
Now, the distance of \[AC\] is given by,
The vertices of A and C are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2,0)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (1, - 3)\] .
\[AC = \sqrt {{{( - 2 - 1)}^2} + {{(0 - ( - 3))}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{( - 3)}^2} + {{(3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {9 + 9} \]
\[ = \sqrt {18} \] units.
As we can see that the distance of the sides AB, BC, and AC are different.
Hence the given triangle is scalene.
So, the correct answer is “the given triangle is scalene”.
Note: Also we know that in equilateral triangles all the angels are the same. In the isosceles triangle only two angles are equal. In scalene all three angels are different. We can differentiate triangles based on angels also. The distance formula is the same for any two points. Do not get confused with the distance formula. The distance formula in above is the same as the \[ = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] . Negative Square is positive.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given vertices are (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (1,-3).
We know that the distance between two points \[({x_1},{y_1})\] and \[({x_2},{y_2})\] is \[ = \sqrt {{{({x_1} - {x_2})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] .
Assume the diagram (for better understanding).

Now we find the distances of AB, AB and BC.
Now, the distance \[AB\] is given by,
The vertices of A and B are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2,0)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (2,3)\]
Substituting we get,
\[AB = \sqrt {{{( - 2 - 2)}^2} + {{(0 - 3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{( - 4)}^2} + {{( - 3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {16 + 9} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25} \]
\[ = 5\] units
Now, the distance of \[BC\] is given by,
The vertices of B and C are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = (2,3)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (1, - 3)\] .
\[BC = \sqrt {{{(2 - 1)}^2} + {{(3 - ( - 3))}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{(1)}^2} + {{(6)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {1 + 36} \]
\[ = \sqrt {37} \] units.
Now, the distance of \[AC\] is given by,
The vertices of A and C are \[({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2,0)\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (1, - 3)\] .
\[AC = \sqrt {{{( - 2 - 1)}^2} + {{(0 - ( - 3))}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{( - 3)}^2} + {{(3)}^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {9 + 9} \]
\[ = \sqrt {18} \] units.
As we can see that the distance of the sides AB, BC, and AC are different.
Hence the given triangle is scalene.
So, the correct answer is “the given triangle is scalene”.
Note: Also we know that in equilateral triangles all the angels are the same. In the isosceles triangle only two angles are equal. In scalene all three angels are different. We can differentiate triangles based on angels also. The distance formula is the same for any two points. Do not get confused with the distance formula. The distance formula in above is the same as the \[ = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] . Negative Square is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




