
The vertical tower stands on a horizontal plane and is surmounted by a vertical flagstaff of height $ 6m $ . At a point on the plane, the angle of elevation of the bottom and the top of the flagstaff are $ 30^\circ $ and $ 60^\circ $ respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the height of the tower. Here, we will construct a figure with the given. As it is a right-angled triangle, we will use trigonometric angles, $ \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $ and $ \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 $ . And eliminate the common side to determine the height of the tower.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to understand the concept, let us construct a figure with the given.
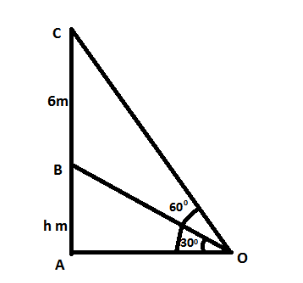
Let $ AB $ be the tower.
And, $ BC $ be a vertical flagstaff of height $ 6m $ .
Therefore, $ BC = 6m $
Let, $ O $ be a point on the plane.
$ \therefore \angle AOB = 30^\circ $ and $ \angle AOC = 60^\circ $
Let the height of the tower, $ AB = h $
Consider $ \Delta AOB $ ,
We know that, $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $
Therefore, $ \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} $
Since $ \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $ and $ AB = h $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
Therefore, $ OA = \sqrt 3 h $
Let this be equation (1)
Now, consider $ \Delta AOC $ ,
We know that, $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $
Therefore, $ \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{AC}}{{OA}} $
We know that,
$ \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 $
And $ AC = AB + BC $
$ \Rightarrow AC = h + 6 $
Now, by substituting the values, we get,
$ \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{OA}} $
Therefore, $ OA = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
Let this be equation (2)
From the equations (1) and (2),
$ \sqrt 3 h = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
$ \sqrt 3 \times \sqrt 3 h = h + 6 $
$ 3h = h + 6 $
$ 3h - h = 6 $
$ 2h = 6 $
$ h = 3 $
Hence, the height of the tower is $ 3m $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 3m $ ”.
Note: In this question it is important to note here that when we are facing these types of questions, we need to construct a figure with the given conditions, and use trigonometric angles. Then eliminate the common side to determine the required answer. Be confident with the trigonometric angles as it is the part where the mistakes occur. Remember that for a right-angled triangle, $ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Hypotenuse}},\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{Hypotenuse}} $ and $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to understand the concept, let us construct a figure with the given.

Let $ AB $ be the tower.
And, $ BC $ be a vertical flagstaff of height $ 6m $ .
Therefore, $ BC = 6m $
Let, $ O $ be a point on the plane.
$ \therefore \angle AOB = 30^\circ $ and $ \angle AOC = 60^\circ $
Let the height of the tower, $ AB = h $
Consider $ \Delta AOB $ ,
We know that, $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $
Therefore, $ \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} $
Since $ \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $ and $ AB = h $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
Therefore, $ OA = \sqrt 3 h $
Let this be equation (1)
Now, consider $ \Delta AOC $ ,
We know that, $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $
Therefore, $ \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{AC}}{{OA}} $
We know that,
$ \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 $
And $ AC = AB + BC $
$ \Rightarrow AC = h + 6 $
Now, by substituting the values, we get,
$ \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{OA}} $
Therefore, $ OA = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
Let this be equation (2)
From the equations (1) and (2),
$ \sqrt 3 h = \dfrac{{h + 6}}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
$ \sqrt 3 \times \sqrt 3 h = h + 6 $
$ 3h = h + 6 $
$ 3h - h = 6 $
$ 2h = 6 $
$ h = 3 $
Hence, the height of the tower is $ 3m $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 3m $ ”.
Note: In this question it is important to note here that when we are facing these types of questions, we need to construct a figure with the given conditions, and use trigonometric angles. Then eliminate the common side to determine the required answer. Be confident with the trigonometric angles as it is the part where the mistakes occur. Remember that for a right-angled triangle, $ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Hypotenuse}},\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{Hypotenuse}} $ and $ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Adjacent}} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




