
The vertical component of velocity of ball with which they are projected
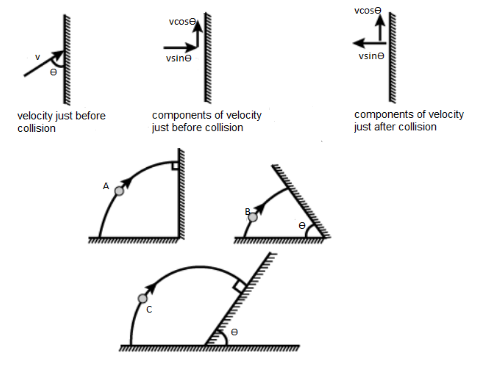
$ \left( A \right)20m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( B \right)10m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( C \right)10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( D \right)undeterminable \\ $

Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint : In order to solve this question, we are going to consider three cases of the projection of the ball of three different orientations. Writing the initial velocities of the ball, their vertical and horizontal components, we analyze the options given for the speeds, and answer the one which suits the best.
The formula for the maximum height is given by
$ h = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} $
Where $ \varphi $ is the angle of projection
The equation third of kinematics
$ {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider that the angle of projection in all the cases be $ \theta $
Now, considering the projection in case $ \left( A \right) $
The initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
The maximum height attained is given by the formula
$ h = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} $
As we know that in the cases of vertical projection or that with an angle, the acceleration value is $ - g $
Now, by the equation third of kinematics,
$ {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \\
\Rightarrow 0 - {u^2}{\sin ^2}\varphi = 2 \times \left( { - g} \right) \times \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} \\ $
Here, the vertical component is $ u{\sin ^2}\varphi $
Now considering the case $ \left( B \right) $
Initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
Resolving the velocity into two components, vertical and horizontal
$ {u_x} = 0 \\
{u_y} = u\sin \varphi \\ $
Now, if we consider the case $ \left( C \right) $
Initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
Resolving it into its components, vertical and horizontal
$ {u_x} = 0 \\
{u_y} = u\sin \varphi \\ $
Now if we take the three options, then all the conditions above are satisfied with the velocity $ 20m{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Hence, option $ A $ is the correct answer.
Note :
The velocity of the ball does not depend on $ \theta $ , in fact it depends only on the initial projection angle as the velocity components, maximum height and the velocity when the trajectory of the ball ends. Hence, the velocity from the options given is tested for all the three cases taken.
The formula for the maximum height is given by
$ h = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} $
Where $ \varphi $ is the angle of projection
The equation third of kinematics
$ {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider that the angle of projection in all the cases be $ \theta $
Now, considering the projection in case $ \left( A \right) $
The initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
The maximum height attained is given by the formula
$ h = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} $
As we know that in the cases of vertical projection or that with an angle, the acceleration value is $ - g $
Now, by the equation third of kinematics,
$ {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \\
\Rightarrow 0 - {u^2}{\sin ^2}\varphi = 2 \times \left( { - g} \right) \times \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\varphi }}{{2g}} \\ $
Here, the vertical component is $ u{\sin ^2}\varphi $
Now considering the case $ \left( B \right) $
Initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
Resolving the velocity into two components, vertical and horizontal
$ {u_x} = 0 \\
{u_y} = u\sin \varphi \\ $
Now, if we consider the case $ \left( C \right) $
Initial velocity,
$ {u_{initial}} = u\sin \varphi $
Resolving it into its components, vertical and horizontal
$ {u_x} = 0 \\
{u_y} = u\sin \varphi \\ $
Now if we take the three options, then all the conditions above are satisfied with the velocity $ 20m{s^{ - 1}} $ .
Hence, option $ A $ is the correct answer.
Note :
The velocity of the ball does not depend on $ \theta $ , in fact it depends only on the initial projection angle as the velocity components, maximum height and the velocity when the trajectory of the ball ends. Hence, the velocity from the options given is tested for all the three cases taken.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




